A) algae
B) fungi
C) animals
D) invertebrates
E) vertebrates
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The chlorophyll a molecules in the reaction center of a photosystem participate directly in the capture of solar energy. What is the purpose of the accessory pigments?
A) They participate in the Calvin cycle.
B) They funnel solar energy to chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
C) They split the water molecule to supply electrons to the chlorophyll a in the reaction center.
D) They change the color of the leaves to discourage predators.
E) They have no purpose.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which steps of photosynthesis does C4 photosynthesis partition in space?
A) carbon fixation and Calvin cycle reactions
B) carbon fixation and light reactions
C) light reactions and Calvin cycle reactions
D) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate G3P) formation and glucose phosphate formation
E) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate BPG) formation and glucose phosphate formation
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
ATP and NADPH are both used during the Calvin cycle. What is the function of each?
A) ATP supplies energy and NADPH supplies electrons for reducing power.
B) ATP supplies energy and NADPH fixes CO2 so it can enter the cycle.
C) Both ATP and NADPH supply energy to the Calvin cycle.
D) NADPH supplies energy and ATP supplies electrons for reducing power.
E) ATP and NADPH are joined into the starter molecule, RuBP, to form glucose.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CAM photosynthesis limits CO2 fixation to nighttime hours in order to
A) allow water to enter leaf spaces during the daylight hours.
B) open stomata only at night, limiting water loss because of heat and low humidity.
C) allow NADPH and ATP to enter leaf spaces.
D) limit the Calvin cycle reactions to nighttime only.
E) limit water uptake from the soil during daytime hours.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The end product of the Calvin cycle reactions is
A) glucose.
B) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate G3P) .
C) sucrose.
D) 3-phosphoglycerate 3PG) .
E) ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate RuBP) .
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Calvin cycle reactions only occur in bundle sheath cells in a C4 plant
A) to shield the Calvin cycle reactions from O2 in the leaf spaces.
B) to allow O2 to enter bundle sheath cells.
C) because rubisco is only found in mesophyll cells.
D) so that they are adjacent to stomata.
E) so that H2O is not available to mesophyll cells.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Not all molecules contain the same amount of chemical energy. What is the energy relationship between G3P and CO2?
A) G3P and CO2 have the same amount of energy.
B) G3P has less energy than CO2.
C) Neither G3P nor CO2 contain any chemical energy.
D) G3P has more energy than CO2.
E) There is not enough information provided to answer the question.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three stages of the Calvin cycle reactions are
A) NADPH reduction, CO2 fixation, and NADP+ regeneration.
B) NADPH reduction, CO2 fixation, and RuBP regeneration.
C) CO2 fixation, CO2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration.
D) CO2 fixation, CO2 reduction, and NADP+ regeneration.
E) CO2 reduction, NADPH reduction, and CO2 regeneration.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The light reactions act much as a battery to power the reactions of the Calvin cycle. This energy is stored as
A) ATP and NADP+.
B) ADP + Pi.
C) ADP + Pi and NADP+.
D) ATP and NADPH.
E) NADPH and NADP+.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the labeled cells of a C3 leaf does not perform photosynthesis? 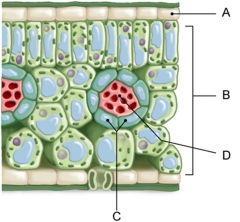
A) A and B
B) A and D
C) B and D
D) B and C
E) C and D
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The light reactions of photosynthesis are said to be similar to a battery because they form a current. In which direction do the electrons of this circuit flow?
A) H2O → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
B) H2O → PSII → chlorophyll b → PSI → chlorophyll a → NADPH
C) NADPH → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADP+
D) NADP+ → PSII → electron transport chain → PSI → electron transport chain → NADPH
E) PSI → electron transport chain → PSII → electron transport chain → NADPH
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which stages of the Calvin cycle reactions require the use of energy from ATP?
A) CO2 fixation and CO2 reduction
B) CO2 reduction and RuBP regeneration
C) CO2 fixation and RuBP regeneration
D) CO2 fixation, CO2 reduction, and RuBP regeneration
E) CO2 reduction and RuBP oxidation
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a disadvantage of C4 photosynthesis relative to C3 photosynthesis?
A) inability of rubisco to obtain O2
B) C4 plants need energy to move fixed carbon compounds into bundle sheath cells
C) need for stomata to close to conserve H2O
D) need for energy to move H2O into bundle sheath cells
E) inability of ATP synthase to utilize H+ gradient for energy
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The O2 given off during photosynthesis is derived from which compound?
A) CO2 and H2O
B) RuBP
C) CO2
D) NADP+
E) H2O
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sucrose, cellulose, amino acids, and starch are all made from what starter molecule in plants?
A) glucose
B) fructose
C) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate G3P)
D) ATP
E) RuBP carboxylase
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a high latitude rainforest, the dominant type of photosynthesis is most likely to be
A) both C3 and CAM.
B) C4.
C) CAM.
D) both C4 and CAM.
E) C3.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why do plants contain other pigments besides chlorophyll?
A) The additional pigments are able to absorb other light wavelengths that chlorophyll cannot.
B) The additional pigments can only absorb violet or ultraviolet light.
C) Chlorophyll is unable to absorb visible light.
D) When chlorophyll breaks down, the additional pigments can absorb the same wavelengths of light.
E) When the additional pigments break down, the chlorophyll can absorb other wavelengths of light. Plants use a variety of pigments in order to absorb a broader portion of the visible light spectrum.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In photosynthesis, the light reactions ________ while the Calvin cycle ________.
A) capture solar energy; converts the captured energy to chemical potential energy
B) can occur only in the light; can occur only in the dark
C) require the presence of ATP; makes ATP
D) can only function if the stomata are open; can only occur if the stomata are closed
E) use products manufactured in the dark reactions; creates products used in the dark reactions
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How does ATP synthase obtain the energy to produce ATP?
A) Hydrogen ions flow down a concentration gradient from the thylakoid space to the stroma through ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + Pi.
B) Water splits, releasing electrons that flow from the stroma to the thylakoid space and attach to the active site of ATP synthase.
C) Electrons from the reaction site center of photosystem II are funneled to ATP synthase, which uses the energy to produce ATP from ADP + Pi.
D) Hydrogen ions in the thylakoid space combine with electrons from the stroma at ATP synthase, releasing energy that can be used to produce ATP from ADP + Pi.
E) A hydrogen ion from NADPH is used by ATP synthase to power the production of ATP from ADP + Pi, and an electron is released, splitting water.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 61
Related Exams