A) Deviations of aggregate supply from long-term growth trends
B) Monetary factors affecting aggregate demand
C) People choosing leisure rather than work
D) A decline in the supply of money
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Taylor rule, if inflation rises by 1 percent above its target of 2 percent, the Fed should:
A) Lower the real Federal funds rate by 0.5 percent
B) Raise the real Federal funds rate by 0.5 percent
C) Lower the money supply by 5 percent
D) Raise the money supply by 5 percent
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mainstream view, the crowding-out effect from the use of fiscal policy is:
A) Small, especially during a recession
B) Large, especially during a recession
C) Large because the velocity of money is high
D) Small because the velocity of money is low
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Crowding-out results from:
A) An increase in the supply of money and a decrease in the velocity of money
B) A decrease in the supply of money and an increase in the velocity of money
C) The inverse relationship between the supply of money and nominal GDP
D) Deficit financing which increases interest rates and reduces investment
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The equation of exchange indicates that an increase in money supply will always lead only to inflation.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If households and firms cut back on spending because they expect other households and firms to do so, and this self-fulfilling prophecy causes a recession, then this would be an example of:
A) Insider-outsider relationships
B) Efficiency wage theory
C) A coordination failure
D) A price-level surprise
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Within the aggregate demand-aggregate supply framework, monetarists argue that a change in aggregate:
A) Demand will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output
B) Demand will have a small effect on the price level, but a permanent effect on output
C) Demand will have a large effect on the price level and a large effect on output
D) Supply will have a large effect on the price level, but a temporary effect on output
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
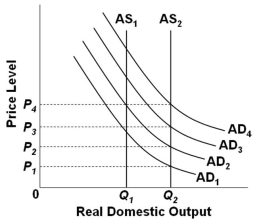 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. If the application of a monetary rule is designed to shift AD1 to AD3, but because of pessimistic business expectations AD1 only shifts to AD2, then mainstream economists would suggest that the actions to be taken to avoid deflation would be to implement a(n) :
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of AD1 and AS1. Suppose that there is economic growth which shifts AS1 to AS2. If the application of a monetary rule is designed to shift AD1 to AD3, but because of pessimistic business expectations AD1 only shifts to AD2, then mainstream economists would suggest that the actions to be taken to avoid deflation would be to implement a(n) :
A) Expansionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
B) Contractionary fiscal policy and a tight money policy
C) Expansionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
D) Contractionary fiscal policy and an easy money policy
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If there is an unanticipated increase in aggregate demand, then according to new classical economics, the economy will self-correct with a(n) :
A) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level, but the price level rises
B) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises
C) Decrease in short-run aggregate supply, so output returns to its initial level and the price level falls
D) Increase in short-run aggregate supply, so output increases and the price level rises
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Most economists today would agree with the view that "money doesn't matter" in macroeconomic theory.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monetarists argue that the amount of money the public will want to hold depends primarily on the level of:
A) Nominal GDP
B) Investment
C) Consumption
D) Prices
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In recent years, calls for monetary rules by the Federal Reserve have been replaced with calls for:
A) A reduction in coordination failures
B) Using an equation of exchange
C) Price-level surprises
D) Inflation targeting
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Monetarists argue that government policy interference in the economy is the primary cause of macroeconomic instability.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which view of the macro economy suggests that the speed of adjustment for self-correction would be very quick?
A) Monetarism
B) Mainstream economics
C) Supply-side economics
D) Rational expectations theory
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mainstream economics views monetary policy as a:
A) Source of instability, similar to the view of monetarism
B) Stabilizing factor, similar to the view of monetarism
C) Source of instability, while monetarism views it as a stabilizing factor
D) Stabilizing factor, while monetarism views it as a source of instability
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mainstream economists have adopted some ideas from RET and some rational expectations assumptions are being incorporated into current macroeconomic models.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the economy diverges from its full-employment output, new classical economics would suggest that:
A) A change in the velocity of money would be all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
B) An improvement in insider-outsider relationships is all that is needed to return it to its full-employment output
C) An efficiency wage in the economy would return it to its full-employment output
D) Internal mechanisms within the economy would automatically return it to its full-employment output
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to rational expectations theory, discretionary monetary and fiscal policy will be ineffective primarily because of the:
A) Successes of macroeconomic policy makers
B) Inability of policy makers to time decisions properly
C) Reaction of the public to the expected effects of policy changes
D) Slow impact of policy to stimulate changes in real output and employment
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the mainstream view, one major source of instability in the macro economy is the volatility of:
A) Product prices
B) Investment spending
C) Consumer spending
D) Labor wages
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
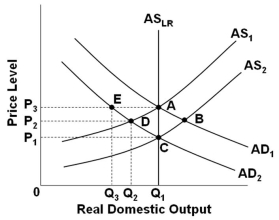 Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices are flexible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point:
Refer to the graph above. Assume that the economy is in initial equilibrium where AD1 intersects AS1. If there is a decrease in aggregate demand to AD2, then according to mainstream economists, if prices are flexible and wages are not, this will result in an equilibrium at point:
A) B
B) C
C) D
D) E
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 134
Related Exams