A) Development genes have no effect on sponges, but control the growth rates of eumetazoans.
B) Development genes are types of biomarkers that develop distinctly with each animal clade.
C) Development genes code for regulation of the body form changes in animals.
D) None of these answer options are correct.
E) Development genes code for proteins that speed up mutation rates in DNA of eumetazoans.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The embryonic germ layer of tissue in animals that develops into the digestive tract,and organs derived from the digestive tract,is the
A) ectoderm.
B) protoderm.
C) mesoderm.
D) pachyderm.
E) endoderm.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A fluid-filled body cavity that forms completely within the mesoderm of animals is a
A) deuterostome.
B) blastula.
C) gastrula.
D) protostome.
E) coelom.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of the echinoderms?
A) They have bilateral symmetry in larvae.
B) They exhibit cephalization.
C) They have spiny skin.
D) They have radial symmetry in adults.
E) They have a complete digestive tract.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer: 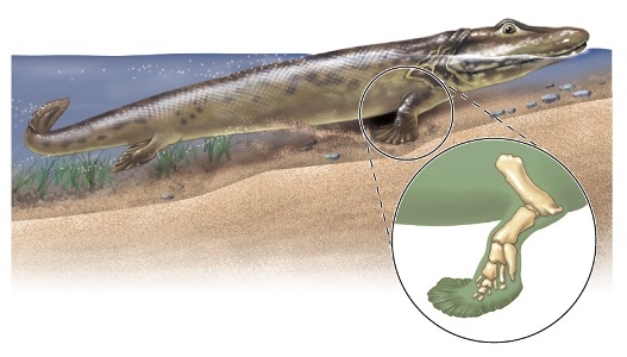 -Tiktaalik either crawled or paddled in shallow tropical streams about 380 MYA,during the late Devonian period.These shallow waters often became anaerobic.What selective advantage would Tiktaalik have under these conditions?
-Tiktaalik either crawled or paddled in shallow tropical streams about 380 MYA,during the late Devonian period.These shallow waters often became anaerobic.What selective advantage would Tiktaalik have under these conditions?
A) It could crawl on shore and feed on birds and reptiles that were on land.
B) It could lift its head out of the water and breathe air through its gills.
C) It could crawl out of the water and walk over to new shallow streams.
D) It could lift its head out of the water and breathe air through its lungs.
E) It could swim better than fish.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mammals that lay eggs are marsupials.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Even semi-aquatic reptiles like crocodiles and alligators can spend much of their life on dry land.Which of the following is an example of an adaptation that would allow reptiles to live and reproduce on dry land?
A) amniotic eggs
B) external fertilization and amniotic eggs
C) internal fertilization and amniotic eggs
D) internal fertilization
E) external fertilization
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An animal that maintains its body temperature by using heat generated from its own metabolism is a(n)
A) thermophile.
B) endotherm.
C) mesophile.
D) amniote.
E) ectotherm.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An animal with an indirect development undergoes a metamorphosis in which larvae do not resemble the adult.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three major body regions of many arthropods are
A) head, gills, and legs.
B) head, thorax, and abdomen.
C) head, gastrovascular cavity, and thorax.
D) head, abdomen, and legs.
E) head, thorax, and legs.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Bats,birds,and dragonflies can all fly.Which of the following groups of animals have some members capable of flight?
A) reptiles and mammals
B) amphibians and arthropods
C) reptiles, amphibians, and arthropods
D) mammals and arthropods
E) reptiles, arthropods, and mammals
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
Main animal groups are noted at the right. Names diverging at each node are morphological or body form names. Note that the animal traits key to distinguishing the groups and body forms are not shown. 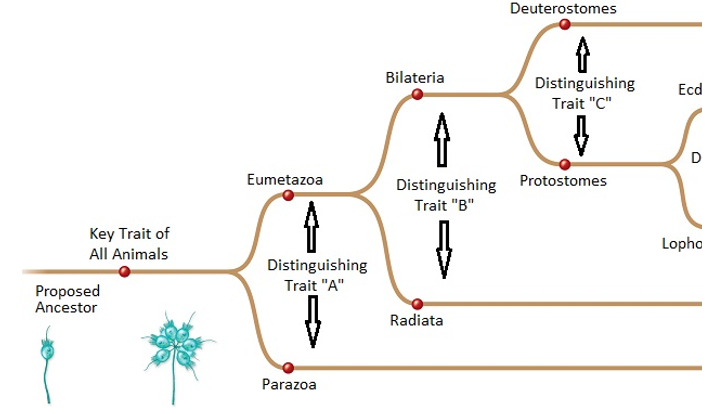 -If an animal is an invertebrate,this means that the animal
-If an animal is an invertebrate,this means that the animal
A) does not have a complete digestive tract.
B) has a backbone.
C) does not have a backbone.
D) does not have true tissues.
E) has a complete digestive tract.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic found among the animals?
A) They have a developmental stage called a blastula.
B) They are multicellular eukaryotes.
C) They are heterotrophs.
D) They secrete and bind to a substance called the extracellular matrix.
E) They form a dikaryotic cell during development.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The free-swimming tunicate larva resembles a tadpole. Once it settles headfirst onto a solid surface the tail and notochord disappear, and the nerve cord shrinks to nearly nothing. The adults, which are usually sessile, retain only the pharyngeal slits. Neither adult nor larva is segmented. -A tunicate is in which group?
A) Nematodes
B) Chordates
C) Mollusks
D) Annelids
E) Echinoderms
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pinworms and hookworms belong to the phylum containing the
A) Flatworms.
B) Cnidarians.
C) Sponges.
D) Nematodes.
E) Annelids.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In most species, the female frog lays her eggs directly in the water as a male clasps her back and releases sperm. The fertilized eggs hatch into legless, aquatic tadpoles. Most tadpoles feed on algae, and have gills. As they mature, tadpoles develop legs and lungs, lose the tail, and acquire carnivorous tastes. -Frogs are in which group?
A) amphibians
B) mammals
C) fishes
D) lancelets
E) reptiles
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a nematode?
A) They have a complete digestive tract.
B) They have bilateral symmetry.
C) They are unsegmented.
D) They have a coelom.
E) They exhibit cephalization.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Sponges belong to the phylum containing the
A) Nematodes.
B) Flatworms.
C) Cnidarians.
D) Annelids.
E) Sponges.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Figuer:
Main animal groups are noted at the right. Names diverging at each node are morphological or body form names. Note that the animal traits key to distinguishing the groups and body forms are not shown.  -Which of the following characteristics do all animals share?
-Which of the following characteristics do all animals share?
A) They are single-celled prokaryotes.
B) They are multicellular prokaryotes.
C) They are single-celled eukaryotes.
D) They are multicellular eukaryotes.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode that scientists have shown grows from a single cell into about 1000 cells,of which the same 80 cells die during development through apoptosis.Studying this process in Caenorhabditis elegans has helped scientists identify the genes that regulate similar processes in humans.Which of the following statements is supported by this observation?
A) Caenorhabditis elegans have all of the same genes as humans.
B) Caenorhabditis elegans give live birth like humans.
C) Caenorhabditis elegans infections in humans trigger apoptosis.
D) Caenorhabditis elegans and humans have a common ancestor.
E) Caenorhabditis elegans has the same organs that are present in humans.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 86
Related Exams