A) With the onset of cleavage
B) At the time of implantation
C) With the establishment of the three primary germ layers
D) When the umbilical cord becomes functional
E) At fertilization
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
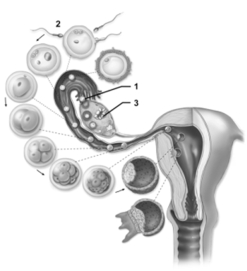 -This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What developmental stage implants in the uterine wall?
-This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What developmental stage implants in the uterine wall?
A) Gastrula
B) Morula
C) Secondary oocyte
D) Blastocyst
E) Zygote
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The two items that form protective layers around the secondary oocyte are the zona pellucida and
A) polar body.
B) transverse membrane.
C) corona radiate.
D) acrosome.
E) primary oocyte.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
It takes about _______ for the placenta to become fully formed.
A) 1 week
B) 2 weeks
C) 1 month
D) 2 months
E) 3 months
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the human,the diploid genetic condition occurs
A) when the number of chromosomes equals the number of genes.
B) when a cell has 23 pairs of chromosomes.
C) when a cell has the (n) number of chromosomes.
D) when a cell has 23 chromosomes.
E) in each gamete just before fertilization.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of possible combinations of genes in humans is virtually limitless.One reason is random assortment of chromosomes and the other is
A) random mating.
B) crossing over.
C) reduction division.
D) nondisjunction.
E) spermiogenesis.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What event does number 1 indicate?
-This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What event does number 1 indicate?
A) Fertilization
B) Implantation
C) Cleavage
D) Gastrulation
E) Ovulation
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why does meiosis pass through two complete cycles?
A) To assure that the gametes will be of the correct size
B) To allow crossing over to occur
C) So that the zygote will have the diploid number of chromosomes
D) Because two cycles are necessary to produce the proper shape of the gametes
E) Because the chromosomes are still double-stranded at the end of meiosis I
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The formation of sex cells in the human is termed
A) gametogenesis.
B) karyogenesis.
C) sporogenesis.
D) typogenesis.
E) differentiation.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A double-stranded chromosome consists of two genetically identical sister chromatids.What important biological event produced the sister chromatids?
A) Crossing over
B) Genetic mutation
C) Mitosis
D) Replication
E) Reduction division
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Spermiogenesis is
A) the formation of a spermatid.
B) the transformation of a spermatid into a functional sperm.
C) the process of a sperm finding an oocyte.
D) reduction division of a spermatogonium.
E) the process of a sperm losing its tail following fertilization.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which primary germ layer is the heart derived?
A) Ectoderm
B) Mesoderm
C) Endoderm
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
B
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fetal period
A) extends from the beginning of the 9th week until birth.
B) extends from the beginning of the 12th week until birth.
C) includes only the middle trimester.
D) includes only the last trimester.
E) extends from the end of the 4th week until birth.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The human sex cells are called
A) spores.
B) germ plasm.
C) genes.
D) gonads.
E) gametes.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is capacitation?
A) Another term for fertilization
B) Implantation of the embryo into the uterine wall
C) Movement of the fertilized egg down the fallopian tube
D) Release of the secondary oocyte from the ovary
E) Conditioning of the sperm within the female reproductive tract
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
E
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The acrosome
A) carries the DNA.
B) is responsible for movement of a spermatozoan.
C) provides nourishment to the sperm.
D) contains enzymes to break through protective layers surrounding the secondary oocyte.
E) initiates growth of the sperm tail.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The process of separating homologous chromosomes is termed
A) replication.
B) reduction division.
C) nondisjunction.
D) cleavage.
E) differentiation.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What event does number 2 indicate?
-This figure shows the transit of the pre-embryo through the uterine tube.What event does number 2 indicate?
A) Fertilization
B) Implantation
C) Cleavage
D) Gastrulation
E) Ovulation
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
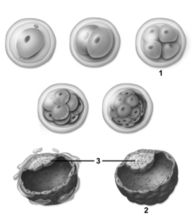 -This figure depicts cleavage.Number 2 indicates a pre-embryo in the _________ stage of development.
-This figure depicts cleavage.Number 2 indicates a pre-embryo in the _________ stage of development.
A) 2-cell
B) 4-cell
C) 8-cell
D) morula
E) blastocyst
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During this critical period the subcutaneous fat is deposited and testes descend into the scrotum.
A) Weeks 1-8
B) Weeks 9-12
C) Weeks 13-16
D) Weeks 17-20
E) Weeks 21-38
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 84
Related Exams