A) the high lipid content of the myelin sheath.
B) their proximity to light-reflecting cartilage.
C) their proximity to white bone.
D) the white color of the perivascular feet.
E) the covering of ependymal cells.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which does not belong to the peripheral nervous system?
A) Ganglion
B) Cranial nerve
C) Spinal cord
D) Peripheral nerve
E) Spinal nerve
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type of neuronal circuit that ensures that we continue to breathe while asleep is a _____________ circuit.
A) converging
B) diverging
C) reverberating
D) parallel-after-discharge
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Of the two types of synapses,based on mode of communication,which is less common but allows faster signal transmission?
A) Chemical synapse
B) Mechanical synapse
C) Physical synapse
D) Magnetic synapse
E) Electrical synapse
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The neurons that are responsible for integrating information by retrieving,processing,storing,and "deciding" how the body responds to stimuli are
A) sensory neurons.
B) motor neurons.
C) accessory neurons.
D) correlation neurons.
E) interneurons.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a type of neuronal pool?
A) Converging
B) Triangular
C) Diverging
D) Parallel-after-discharge
E) Reverberating
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which glial cell myelinates and insulates axons in the peripheral nervous system?
A) Astrocyte
B) Ependymal cell
C) Neurolemmocyte
D) Microglial cell
E) Oligodendrocyte
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structures extend into the axon and dendrite of a neuron to provide tensile strength?
A) Motor filaments
B) Nissl bodies
C) Telodendria
D) Neurofibrils
E) Collateral fibers
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Axons terminate at each of these locations except
A) other neurons.
B) bone.
C) smooth muscle cells.
D) glands.
E) skeletal muscles cells.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not a step in the process of Wallerian degeneration?
A) Neurolemmocytes form regeneration tube.
B) Proximal portion of severed axon seals off.
C) Effector is reinnervated.
D) Macrophages remove debris.
E) No exceptions;all of these are steps in the process.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Neural stem cells in the CNS
A) have no known function.
B) can only form glial cells.
C) can form new neurons throughout the CNS.
D) can form new neurons in only certain portions of the CNS such as the hippocampus.
E) can migrate to the PNS as needed.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which is not characteristic of neurons?
A) High mitotic rate
B) High metabolic rate
C) Require continuous supplies of glucose and oxygen
D) Extreme longevity
E) No exceptions;all of these are characteristic of neurons
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of circuit is used to maintain body posture while walking?
A) Converging
B) Diverging
C) Reverberating
D) Parallel-after-discharge
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The most abundant glial cell in the CNS is the
A) astrocyte.
B) ependymal cell.
C) neurolemmocyte.
D) microglial cell.
E) oligodendrocyte.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The epineurium is composed of
A) dense regular connective tissue.
B) simple squamous epithelium.
C) dense irregular connective tissue.
D) areolar connective tissue.
E) pseudostratified nonkeratinized epithelium.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
As the distance between a damaged axon and its receptor organ increases,the possibility of repair increases.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This condition is a disorder of the peripheral nervous system characterized by muscle weakness that begins in the distal limbs,but rapidly advances to involve proximal muscles as well.
A) Guillain-Barré syndrome
B) Parkinson disease
C) Multiple sclerosis
D) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
E) None of the choices is correct.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure does number 5 indicate? 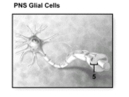
A) Neurofibril node
B) Myelin sheath
C) Nucleus
D) Perivascular foot
E) Ependymal cell
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This figure depicts a typical neuron.What structures are indicated by number 1? 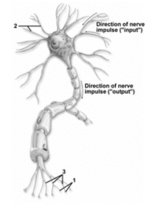
A) Axon hillocks
B) Dendrites
C) Axon collaterals
D) Telodendria
E) Synaptic knobs
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The glial cell that helps to circulate cerebrospinal fluid is the
A) astrocyte.
B) ependymal cell.
C) neurolemmocyte.
D) microglial cell.
E) oligodendrocyte.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 93
Related Exams