A) the fundamental niche is the actual niche that a species occupies while the realized niche is not.
B) the fundamental niche is the entire niche that a species is capable of using while the realized niche is just what is being occupied.
C) the fundamental niche is smaller than the realized niche.
D) the realized niche is theoretical while the fundamental niche is the entire niche that an organism can use.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Animals defend themselves against predators by all of the following except
A) warning coloration.
B) cryptic coloration.
C) chemical defenses such as poisons and stings.
D) parasitism.
E) aposematic coloration.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
No two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely without competition driving one to _________.
A) migrate
B) overpopulate
C) speciation
D) extinction
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In this relationship,one organism serves as a host to another organism,usually to the host's disadvantage.
A) predation
B) parasitism
C) mutualism
D) commensalism
E) symbiotic
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the fundamental and realized niche is false?
A) A species' realized niche could be the same size as its fundamental niche.
B) A species' realized niche could be smaller than its fundamental niche.
C) A species' fundamental niche can be smaller than its realized niche.
D) The extent of the realized niche is determined,in part,by intraspecific completion.
E) The extent of the fundamental niche is determined,in part,by conditions of the physical environment.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The way in which an organism utilizes its environment may be called
A) resource partitioning.
B) its habitat.
C) competitive exclusion.
D) intraspecific competition.
E) its nichE.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You collect data on growth of two different species (A and B) when grown by themselves and with each other.Which one of the following comparisons would best show the effect of only interspecific on species B?
A) the growth of species A when with species B
B) the growth of species B when with species A
C) the growth of species B alone with its grown when with A
D) the growth of species A alone with its grown when with B
E) the growth of species A with B compared with the growth of species B with A
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The dynamic processes that are of critical importance in succession involve all of the following except
A) tolerance.
B) facilitation.
C) inhibition.
D) competitive exclusion.
E) disturbancE.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cattle egrets follow African ungulates such as African buffalo around and catch insects that the buffalo flush.Oxpeckers perch on the backs of buffalo and feed on ectoparasites that infest the buffalo.Which one of the following shows the ecological interaction that the buffalo has with each bird?
A) cattle egret: mutualism;oxpecker: commensalism
B) cattle egret: commensalism;oxpecker: mutualism
C) cattle egret: competition;oxpecker: mutualism
D) cattle egret: mutualism;oxpecker: mutualism
E) cattle egret: commensalism;oxpecker: commensalism
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two of Darwin's finches display a character displacement when they occur as sympatric species.Which of the statements correctly interprets the graph? 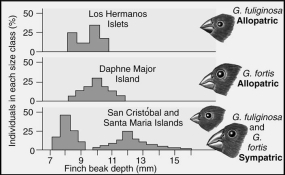
A) Both species have the same size beak on Santa Maria Island.
B) Both species have the same size beaks on Daphne Major.
C) Both species have the same size beaks on Los Hermanos Island.
D) The two species have different beak sizes when they occur on the same islanD.
E) The two species feed on different food resources;one feeds on seeds while the other feeds on insects.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Succession happens because species in the habitat alter that habitat in ways that assist other species.There are three dynamic concepts that are of critical importance for succession to take place.They are
A) facilitation,inhibition,and tolerance.
B) symbiotic relationships,facilitation,and aposematic coloration.
C) mimicry,coevolution,and competitive exclusion.
D) competition,climax communities,and tolerance.
E) competition,inhibition,and coevolution.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alligators excavate holes in the bottom of bodies of water.During times of severe drought these holes act as refugia for various aquatic organisms that might perish if there were no water available.Thus,alligators in this system can be classified as a(n)
A) keystone species.
B) symbiotic species.
C) sympatric species.
D) allopatric species.
E) refugistic species.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In studies of two species of barnacles in the marine intertidal zone it was observed that Chthamalus can live in the upper intertidal zone and the lower intertidal zone if Semibalanus is absent,and Semibalanus can only live in the lower zone because it is more subject to dehydration.Based on this,which of the following statements is false?
A) The realized niches of the two species differ.
B) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than its realized niche.
C) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than the fundamental niche of Semibalanus.
D) The fundamental and the realized niches of Chthamalus are the same.
E) The fundamental and the realized niches of Semibalanus are the samE.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The pattern of living or the function of an organism in a community is called its
A) niche.
B) habitat.
C) hierarchy.
D) speciation.
E) predation.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement is the correct interpretation of the graph? 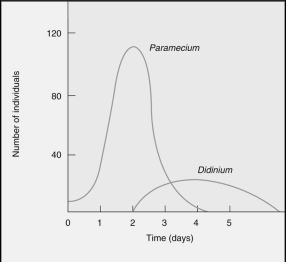
A) The population of Didinium goes extinct with the addition of Paramecium on day 4.
B) The population of Didinium continues to increase and remains high even after the extinction of the Paramecium.
C) The population of Paramecium goes extinct with the addition of Didinium on day 8.
D) The population of Didinium increased but then went extinct after the population of Paramecium went extinct.
E) The population of Didinium is able to increase at the expense of the Paramecium population.After a brief period both populations are able to coexist.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement correctly interprets the graph? 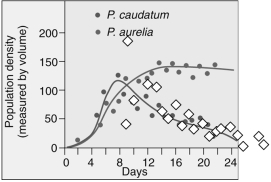
A) Paramecium caudatum drives Paramecium aurelia to near extinction.
B) Paramecium aurelia drives Paramecium caudatum to near extinction.
C) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are able to compete for the same resource and their population densities are not affected.
D) Paramecium caudatum and Paramecium aurelia are unable to exist and both populations go extinct after 24 days.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemical defenses are found in all of the following except
A) marine animals.
B) insects.
C) plants.
D) snakes,spiders,and fishes.
E) Batesian mimics.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cardiac glycosides,molecules causing a drastic effect on vertebrate heart function,are produced as defense chemicals by plants,which belong to
A) the milkweed and dogbane families.
B) the mustard family.
C) grasses.
D) poison ivy,oak,and sumac.
E) the bean family.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are types of symbiosis except
A) commensalism.
B) camouflage.
C) predation.
D) parasitism.
E) mutualism.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A species that interacts in critical ways with many other elements of an ecosystem is called a ___________ species.
A) predatory
B) keystone
C) primary
D) dominant
E) succeeding
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 74
Related Exams