B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 10-1
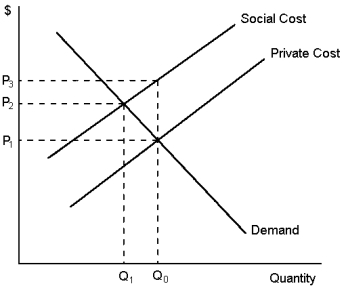 -Refer to Graph 10-1. In the figure shown the marginal:
-Refer to Graph 10-1. In the figure shown the marginal:
A) benefit of the positive production externality is measured by P3 - P1
B) cost of the negative production externality is measured by P3 - P2
C) cost of the negative production externality is measured by P3 - P1
D) cost of the negative production externality cannot be measured
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is impossible to prohibit all polluting activity.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Some economists believe that technology spillovers are pervasive and industries with the largest spillovers should be encouraged.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 10-4
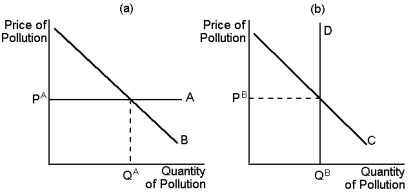 -Referring to Graph 10-4, which curve best represents a Pigovian tax?
-Referring to Graph 10-4, which curve best represents a Pigovian tax?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following could be associated with positive consumption externalities? (i) child immunisations (ensuring that the general population is vaccinated against communicable diseases) (ii) alcohol consumption (iii) maintaining the appearance of historic buildings
A) (i) , (ii) and (iii)
B) (ii) and (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) and (ii) only
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 10-1
 -Refer to Graph 10-1. This graph reflects the presence of a:
-Refer to Graph 10-1. This graph reflects the presence of a:
A) negative production externality
B) positive production externality
C) negative consumption externality
D) positive consumption externality
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the absence of public policies, markets will ensure that:
A) demand will always reflect all positive externalities in consumption
B) demand will always reflect all negative externalities in consumption
C) supply will always reflect all negative and/or positive externalities in production
D) none of the above holds true
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pigovian taxes are typically advocated to correct for the effects of:
A) positive externalities
B) negative externalities
C) regulatory burden
D) all of the above
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Negative consumption externalities will have a socially optimal quantity that is smaller than the quantity determined by the private market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that water pollution creates a negative production externality on a local fishing firm. This means:
A) the fishing firm will catch as less fish than before at the same cost
B) it will be socially optimal for the water pollution to be eliminated
C) it will be socially optimal to do nothing about the water pollution
D) the fishing firm will catch more fish than before at the same cost
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nancy loves to landscape her yard, but her neighbour Tom places a low value on his landscaping. When Tom's grass is neglected and gets long, Nancy will mow it for Tom. This is an example of:
A) a situation in which the Coase theorem fails to explain the law mowing arrangement
B) improper allocation of resources
C) a private solution to a negative externality problem
D) an exploitation of a common resource
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one problem that keeps people from privately solving externalities?
A) each party involved holds out for a better deal
B) an efficient bargain price is unattainable
C) only problems with a sufficiently large number of parties can be solved
D) there is a lack of government intervention
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Children can be thought of as imposing negative externalities on aeroplane passengers because:
A) when they cry, passengers bear a portion of the cost of this discomfort
B) their tickets are free or obtained at reduced cost
C) children (and their parents) are typically isolated in the rear of the airplane
D) all of the above are true
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the government were to limit the release of air pollution produced by a steel mill to 10 000 units, this policy would be considered a:
A) regulation
B) Pigovian tax
C) subsidy
D) market-based policy
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A Pigovian tax:
A) allocates pollution to those factories that face the highest cost of reducing it
B) is a form of regulation
C) works well for all types of externalities
D) is deemed inferior to regulatory policy by most economists
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following are characteristics of tradeable pollution permits? (i) they are a scarce resource (ii) they can be traded in a market governed by supply and demand (iii) they eventually lead to an efficient elimination of all pollution
A) (i) , (ii) and (iii)
B) (iii) only
C) (i) and (iii) only
D) (i) and (ii) only
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pollution:
A) should be corrected by the subsidisation of polluting firms
B) is not an economic problem because it is external to the market system
C) is a common example of private production costs
D) is a common example of a negative externality
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Technology spillover occurs when:
A) the firm's innovations allow it to establish monopoly power
B) new products by high-tech firms create harmful wastes
C) research by a firm creates innovations that are easily applied and used by others
D) patent laws are used to hinder other firms adopting new technology
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Graph 10-5
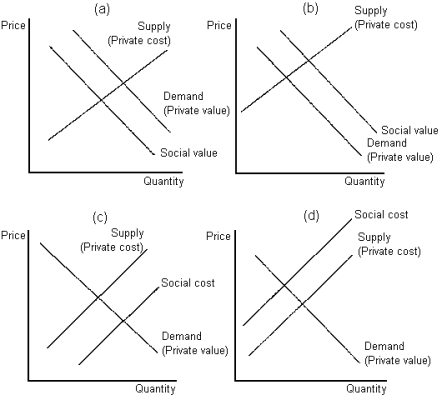 -Refer to Graph 10-5. Which of the graphs shown best depicts the case of a positive consumption externality?
-Refer to Graph 10-5. Which of the graphs shown best depicts the case of a positive consumption externality?
A) panel (a)
B) panel (b)
C) panel (c)
D) panel (d)
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 199
Related Exams