A) 2 million.
B) 3 billion.
C) 4 billion.
D) 7 billion.
E) 10 billion.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ecological footprint is a construct that is useful
A) for a person living in a developed nation to consider to make better choices when using global food and energy resources.
B) for a person living in a developing country to see how much of the world's resources are left for him/her.
C) in converting human foods' meat biomass to plant biomass.
D) in making predictions about the global carrying capacity of humans.
E) in determining which nations produce the least amount of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the survivorship curves shown below to answer the following questions.
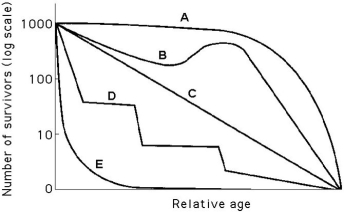 -Which curve best describes survivorship in humans who live in undeveloped nations?
-Which curve best describes survivorship in humans who live in undeveloped nations?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Elephants and sea turtles are both long-living vertebrates.What type of survivorship curve would you expect to see for these two species,respectively?
A) Type 1 and Type1
B) Type 1 and Type111
C) Type 1 and Type11
D) Type 11 and Type11
E) Type 111 and Type111
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Please read the paragraph below and review the figure to answer the following question.
Researchers in the Netherlands studied the effects of parental care given in European kestrels over five years.The researchers transferred chicks among nests to produce reduced broods (three or four chicks) ,normal broods (five or six chicks) ,and enlarged broods (seven or eight chicks) .They then measured the percentage of male and female parent birds that survived the following winter.(Both males and females provide care for chicks.)
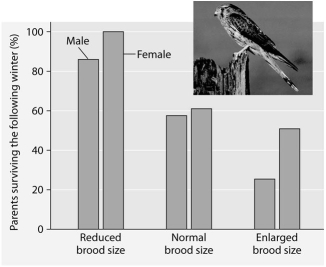 Brood size manipulations in the kestrel: Effects on offspring and parent survival.
-Which of the following is a conclusion that can be drawn from this graph?
Brood size manipulations in the kestrel: Effects on offspring and parent survival.
-Which of the following is a conclusion that can be drawn from this graph?
A) Female survivability is more negatively affected by larger brood size than is male survivability.
B) Male survivability decreased by 50% between reduced and enlarged brood treatments.
C) Both males and females had increases in daily hunting with the enlarged brood size.
D) There appears to be a negative correlation between brood enlargements and parental survival.
E) Chicks in reduced brood treatment received more food, weight gain, and reduced mortality.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Allee effect is used to describe a population that
A) has become so small that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
B) has become so large that it will have difficulty surviving and reproducing.
C) is viable and stable at its carrying capacity.
D) has exceeded its carrying capacity.
E) is in crash decline.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely to contribute to density-dependent regulation of populations?
A) the removal of toxic waste by decomposers
B) intraspecific competition for nutrients
C) earthquakes
D) floods
E) fires
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The following questions refer to the figure below,which depicts the age structure of three populations.
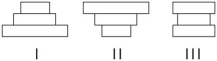 -Assuming these age-structure diagrams describe human populations,which population(s) is (are) likely to experience zero population growth (ZPG) ?
-Assuming these age-structure diagrams describe human populations,which population(s) is (are) likely to experience zero population growth (ZPG) ?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I and II
E) II and III
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an example of density-dependent regulation?
A) competition and predation
B) intrinsic physiological factors
C) territoriality
D) disease
E) a severe frost
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the equation for zero population growth (ZPG) ?
A) R = b - m
B) dN/dt = rN
C) dN/dt = rmₐₓ N (K - N) /K
D) dN/dt = rmₐₓ N
E) dN/dt = 1.0N
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In 2008,the population of New Zealand was approximately 4 275 000 people.If the birth rate was 14 births for every 1000 people,approximately how many births occurred in New Zealand in 2008?
A) 6000
B) 42 275
C) 60 000
D) 140 000
E) 600 000
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the most important assumption for the capture-recapture method to estimate the size of wildlife populations?
A) All females in the population have the same litter size.
B) More individuals emigrate from, as opposed to immigrate into, a population.
C) Over 50% of the marked individuals need to be trapped during the recapture phase.
D) There is a 50:50 ratio of males to females in the population before and after trapping and recapture.
E) Marked individuals have the same probability of being recaptured as unmarked individuals during the recapture phase.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is characteristic of K-selected populations?
A) offspring with good chances of survival
B) many offspring per reproductive episode
C) small offspring
D) a high intrinsic rate of increase
E) early parental reproduction
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting from a single individual,what is the size of a population of bacteria that reproduce by binary fission every 20 minutes at the end of a 2-hour time period? (Assume unlimited resources and no mortality.)
A) 6
B) 18
C) 128
D) 512
E) 1024
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following life history traits is incorrectly matched?
A) r selection-density dependent selection
B) semelparity-a one-shot, large reproductive effort
C) iteroparity-relatively few but large offspring are produced at each reproduction
D) semelparity-recorded in Pacific salmon
E) life history traits-are trade-offs between conflicting demands
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A population of ground squirrels has an annual per capita birth rate of 0.06 and an annual per capita death rate of 0.02.Calculate an estimate of the number of individuals added to (or lost from) a population of 1000 individuals in one year.
A) 120 individuals added
B) 40 individuals added
C) 20 individuals added
D) 400 individuals added
E) 20 individuals lost
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Uniform spacing patterns in birds,such as albatrosses,are often associated with
A) patterns of rock outcrops.
B) antagonistic social interactions between individuals of the population.
C) the uniform distribution of nesting material.
D) the concentration of prey within the population's range.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Natural selection involves energetic trade-offs between
A) choosing how many offspring to produce over the course of a lifetime and how long to live.
B) producing large numbers of gametes when employing internal fertilization versus fewer numbers of gametes when employing external fertilization.
C) the emigration of individuals when they are no longer reproductively capable or committing suicide.
D) increasing the number of individuals produced during each reproductive episode with a corresponding decrease in parental care.
E) high survival rates of offspring and the cost of parental care.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following could be a density-independent factor limiting human population growth?
A) social pressure for birth control
B) earthquakes
C) plagues
D) famines
E) pollution
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is territoriality an adaptive behaviour for songbirds maintaining populations at or near their carrying capacity?
A) Songbirds expend a tremendous amount of energy defending territories so that they spend less time feeding their young and fledgling mortality increases.
B) Only the fittest males defend territories and they attract the fittest females so the best genes are conveyed to the next generation.
C) Songbird males defend territories commensurate with the size from which they can derive adequate resources for themselves, their mate, and their chicks.
D) Many individuals are killed in the agonistic behaviours that go along with territorial defence.
E) Adult songbirds make improvements to the territories they inhabit so that they can produce successfully fledged chicks.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 89
Related Exams