A) There would have been no bacterial colonies on the master plate or on the plates with the T1 phage.
B) There would have been no bacterial colonies on the master plate,but there would have been copious amouts on the plates with the T1 phage.
C) There would be bacterial colonies on the master plate and there would be a few colonies growing on plates with the T1 phage,but the two plates with T1 phage would have colonies growing in different locations.
D) There would have been bacterial colonies on the master plate and all of those colonies would be present on the plates with the T1 phage.
E) You would need to design a completely different experiment to test Lamarck's hypothesis.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At what phase of the cell cycle does p53 halt cell division if it senses DNA damage?
A) S
B) G2
C) M
D) G0
E) G1
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Study the mutations described below and determine which one is most likely to lead to cancer.
A) A mutation in the Ras protein increases its affinity for GDP.
B) A mutation in the Ras protein that prevents GTP hydrolysis.
C) A mutation in a receptor protein that decreases its affinity for a growth factor.
D) A mutation in a transcription factor that prevents it from binding to the DNA to transcribe genes that promote cell division.
E) All of these mutations might lead to cancer.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Somatic cell mutations are heritable.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following LEAST belongs with the others?
A) Ras protein
B) UvrA protein
C) UvrD protein
D) UvrC protein
E) DNA Polymerase
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
_______ can convert proto-oncogenes into oncogenes.
A) Gene amplifications
B) Chromosomal translocations
C) Missense mutations
D) All of these choices are correct
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A repair enzyme recognizes an incorrect structure in the DNA and directly converts it back to the correct structure.Which of the following DNA repair systems is responsible for the correction?
A) base excision repair
B) direct repair
C) indirect repair
D) nucleotide excision repair
E) mismatch repair
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are chemical mutagens EXCEPT
A) nitrogen mustard.
B) X-rays.
C) ethyl methanesulfonate.
D) benzo(a) pyrene.
E) nitrous acid.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following proteins is responsible for advancing a cell through the four phases of the cell cycle?
A) caspases
B) cyclins
C) claudins
D) endonucleases
E) cofactors
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cells are normally limited to one DNA repair system that corrects DNA mistakes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the Ames test,mutagenicity is normally tested on a strain of bacterium (Salmonella typhimurium) that cannot synthesize the amino acid histidine.Therefore,these bacteria require histidine in the growth plate to survive.A researcher performs the Ames test to evaluate the mutagenicity of a newly synthesized compound and notices that in the presence of the new compound,several colonies of Salmonella typhimurium is living on the histidine-free growth plate.What can be assumed from these results?
A) The newly synthesized compound induced a mutation in the bacteriA.
B) The bacteria no longer produce histidine.
C) The bacteria now produce histidine.
D) The newly synthesized compound induced a mutation in the bacteria and the bacteria no longer produce histidine.
E) The newly synthesized compound induced a mutation in the bacteria and the bacteria now produce histidinE.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cancers originate from a single cell.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mutation causes a gene to become overactive,contributing to uncontrolled cell growth.Which term best describes this gene?
A) tumor-suppressor gene
B) oncogene
C) spliced gene
D) alternatively spliced gene
E) malignant gene
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The timing of a mutation during development has negligible effects on the severity of the genetic defect.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Study the loci that have been identified on the two non-homologous chromosomes below and determine what mutation is the most likely to lead to cancer. 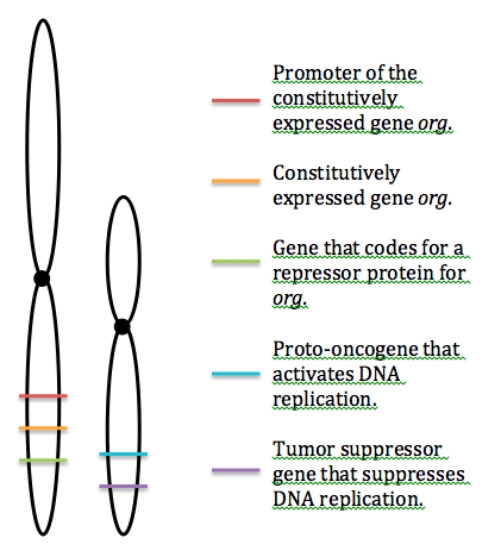
A) A reciprocal translocation switches the entire long arm of one chromosome with the entire long arm of the other chromosome.
B) An inversion switches the position of the blue and purple genes.
C) An inversion switches the position of the red and orange regions.
D) A deletion occurs in the green gene,so that it no longer binds to org,but instead binds to the purple gene.
E) A deletion occurs in the green gene,so that it no longer binds to org,but instead binds to the blue genE.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The movement of DNA polymerase continues unimpeded if a thymine dimer is present in the DNA double helix.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ionizing radiation can produce which of the following?
A) cytosine
B) free radicals
C) stop codons
D) thymine dimers
E) hypoxanthine
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following diseases is associated with faulty DNA repair mechanisms?
A) Alzheimer's disease
B) diabetes
C) xeroderma pigmentosum
D) diabetes and xeroderma pigmentosum
E) Alzheimer's disease and diabetes
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A gene created from the fusion of two gene fragments is considered a
A) tumor-suppressor gene.
B) proto-oncogene.
C) structural gene.
D) regulatory gene.
E) chimeric genE.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What would result from a single nucleotide deletion (point mutation) within the coding sequence of a structural gene?
A) a silent point mutation with no deleterious effects
B) a missense point mutation resulting in the change of one amino acid
C) a nonsense point mutation resulting in the generation of a premature stop codon
D) a frameshift mutation,producing a completely different amino acid sequence
E) All of the choices are possiblE.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 48
Related Exams