A) profit-maximizing price only
B) both profit-maximizing price and fair-return prices
C) both fair-return price and the socially optimal prices
D) all three: profit-maximizing, fair return, and socially optimal prices
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
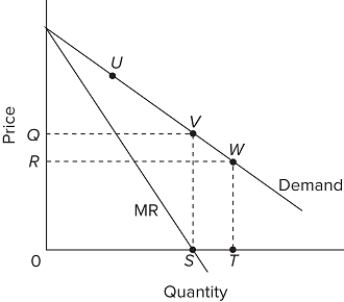 Refer to the graph, which shows a linear demand curve for a monopolist. In which range of the demand curve (or output quantity) will the firm operate?
Refer to the graph, which shows a linear demand curve for a monopolist. In which range of the demand curve (or output quantity) will the firm operate?
A) to the right of point W
B) between V and W
C) between S and T
D) between quantities 0 and S
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
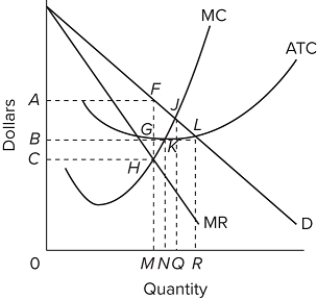 Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm's economic profit will be BAFG.
Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At the profit-maximizing output, the firm's economic profit will be BAFG.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
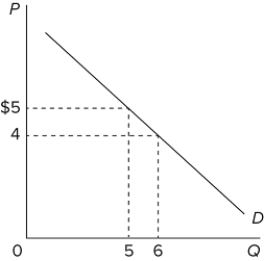 The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is
The diagram indicates that the marginal revenue of the sixth unit of output is
A) −$1.
B) $1.
C) $4.
D) $24.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopolist engages in price discrimination, it will
A) realize a smaller profit.
B) charge a higher price where individual demand is inelastic and a lower price where individual demand is elastic.
C) produce a smaller output than when it did not discriminate.
D) charge a competitive price to all its customers.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
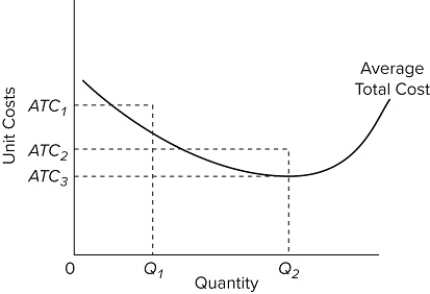 Refer to the long-run cost curve for a firm. If the firm produces output Q₁ at an average total cost of ATC₁, then the firm is
Refer to the long-run cost curve for a firm. If the firm produces output Q₁ at an average total cost of ATC₁, then the firm is
A) producing the profit-maximizing output but is failing to minimize production costs.
B) incurring X-inefficiency but is realizing all existing economies of scale.
C) incurring X-inefficiency and is failing to realize all existing economies of scale.
D) producing that output with the most efficient combination of inputs and is realizing all economies of scale.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
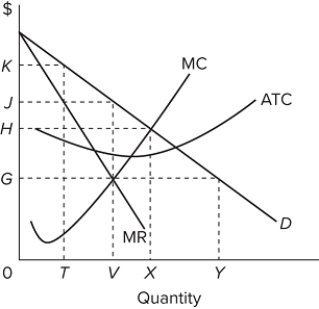 Refer to the graph for a profit-maximizing monopolist. At equilibrium, the firm will be earning
Refer to the graph for a profit-maximizing monopolist. At equilibrium, the firm will be earning
A) positive profits.
B) negative profits.
C) zero profits.
D) profits that cannot be determined from the given graph.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To practice long-run price discrimination, a monopolist must
A) be a natural monopoly.
B) charge one price to all buyers.
C) permit the resale of the product by the original buyers.
D) be able to separate buyers into different markets with different price elasticities.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the inelastic portion of a monopolist's demand curve, an increase in price will
A) reduce output quantity, increase total revenue, and increase total cost.
B) reduce output quantity, increase total revenue, and decrease total cost.
C) raise output quantity, decrease total revenue, and increase total cost.
D) reduce output quantity, decrease total revenue, and decrease total cost.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
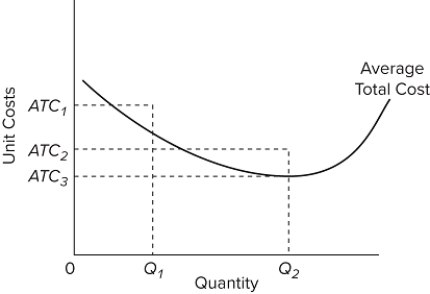 Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q ₂ at an average cost of ATC ₂, then the firm is
Refer to the long-run cost diagram for a firm. If the firm produces output Q ₂ at an average cost of ATC ₂, then the firm is
A) producing the profit-maximizing output but is failing to minimize production costs.
B) incurring X-inefficiency but is producing that output at which all existing economies of scale might be realized.
C) incurring X-inefficiency and is failing to produce the output at which all economies of scale might be realized.
D) producing that output with the most efficient combination of inputs and is realizing all existing economies of scale.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For a pure monopolist, the relationship between total revenue and marginal revenue is such that
A) marginal revenue is positive when total revenue is at a maximum.
B) total revenue is positive when marginal revenue is increasing, but total revenue becomes negative when marginal revenue is decreasing.
C) marginal revenue is positive when total revenue is increasing, but marginal revenue becomes negative when total revenue is decreasing.
D) marginal revenue is positive so long as total revenue is positive.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
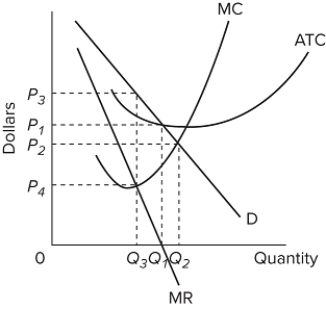 Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at
A) P₁.
B) P₃.
C) P₂.
D) P₄.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
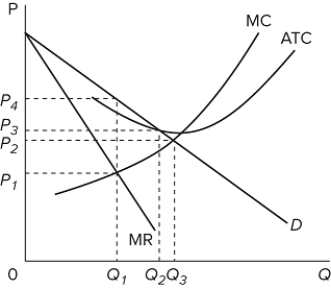 Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. If the government regulated the monopoly and made it charge the socially optimal price, this price would be
Refer to the graph for a pure monopoly. If the government regulated the monopoly and made it charge the socially optimal price, this price would be
A) higher than the profit-maximizing price.
B) higher than the fair-return price.
C) lower than both the fair-return price and the profit-maximizing price.
D) between the fair-return price and the profit-maximizing price.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination is more common in service industries because
A) low-price buyers will find it virtually impossible to resell the products of such industries to high-price buyers.
B) the costs of providing such industries' products to different groups of buyers vary dramatically.
C) the price elasticity of demand is the same for all groups of buyers in these industries.
D) all firms in these industries have significant monopoly power over price.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
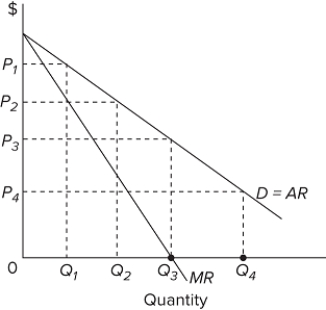 Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. Total revenue will be greatest at what output level?
Refer to the graph, which shows the revenue curves for a monopolist. Total revenue will be greatest at what output level?
A) Q₁
B) Q₂
C) Q₃
D) Q₄
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An important economic problem associated with pure monopoly is that, at the profit-maximizing outputs, resources are
A) overallocated because price exceeds marginal cost.
B) overallocated because marginal cost exceeds price.
C) underallocated because price exceeds marginal cost.
D) underallocated because marginal cost exceeds price.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Compared to the purely competitive industry, a pure monopoly
A) is able to use barriers to entry and maintain positive economic profits in the long run.
B) produces an equal amount of output, but charges higher prices to cover all costs in the market.
C) is often more efficient from society's perspective because it has big plants and it uses the newest technology.
D) will always become competitive in the long run because positive economic profits will entice competitors into the market.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
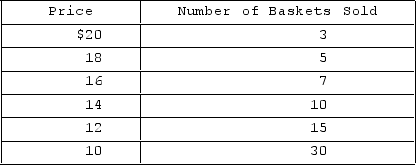 The table shows the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets. What is the change in total revenue if she lowers the price from $20 to $18?
The table shows the demand schedule facing Nina, a monopolist selling baskets. What is the change in total revenue if she lowers the price from $20 to $18?
A) $10
B) $20
C) $30
D) $40
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The government may create barriers to entry that serve to foster monopoly power of firms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The supply curve for a monopolist is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the average variable cost curve.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 407
Related Exams