A) when the demand for its product or service is inelastic.
B) if it is producing an inferior good.
C) if economies of scale are experienced over the full range of output.
D) because government grants it an exclusive franchise.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Google was fined $5 billion by European Union antitrust officials for
A) conspiring with Microsoft to ensure that Google and Microsoft products were bundled.
B) coercing smartphone manufacturers to install Google search bars over competing companies search bars.
C) using pricing algorithms to price-fix with other Internet sellers.
D) using its monopoly power to require all computers sold in Europe to support Google Chrome.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The theory of regulation developed to deal with "natural monopolies" is called
A) legal cartel theory.
B) public interest theory.
C) potential competition theory.
D) social regulation theory.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following beliefs is not strongly espoused by the "laissez-faire perspective" in antitrust policy?
A) Competition among firms is a battle for dominance.
B) The focus of antitrust policy should be on market structure rather than behavior.
C) Competition and creative destruction could lead to monopolies.
D) Monopoly pricing and profits create incentives for firms that are economically beneficial.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Antitrust policy pertains to government regulation of firms' prices within selected industries, such as utilities.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Consider This box "Of Sea Fish and eBooks (and Other Things in Common) ", which of the following firms were convicted for horizontal price-fixing?
A) Dell and Gateway (personal computer makers)
B) Boeing and Airbus (aircraft manufacturers)
C) Heinz and Del Monte (food product firms)
D) Apple, Harper Collins, and Penguin (e-books)
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The effectiveness of regulation is sometimes criticized because
A) regulators try to please everybody.
B) of the high profits in regulated industries.
C) regulators don't know how to regulate industries.
D) regulators usually have been closely associated with the industries they regulate.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which antitrust act provided that injured parties could file suit and, if successful, collect triple damages from monopolistic violators?
A) Wheeler-Lea Act
B) Clayton Act
C) Sherman Act
D) Celler-Kefauver Act
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Laws and government actions designed to prevent monopoly and to promote competition are the focus of
A) social regulation.
B) industrial regulation.
C) antitrust policy.
D) incomes policy.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sum of the squared values of market shares of firms in an industry is referred to as the
A) concentration ratio.
B) Herfindahl index.
C) variance value.
D) antitrust index.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Celler-Kefauver Act made vertical mergers legal, provided each firm does not have more than 30 percent of its relevant market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that you own a toy store and want to buy 100 talking robots. Your supplier will sell you the robots only if you also agree to buy 200 dolls. This is an illegal practice called
A) monopolistic.
B) a tying contract.
C) a cartel.
D) discriminatory.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following findings would be the most likely to lead the U.S. Justice Department to block a corporate merger under terms of the Clayton Act?
A) a buyer-seller relationship between the two firms
B) a high pre-merger Herfindahl index in the industry and a large boost in the index because of the merger
C) a low pre- and post-merger concentration ratio in the industry
D) evidence that one of the firms is highly unprofitable
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Per se violations in antitrust law refer to
A) activities that are illegal in and of themselves.
B) violations that are alleged but not yet proven.
C) cases that are subject to the rule of reason.
D) antitrust cases that are pending resolution.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a primary concern of social regulation?
A) price-fixing
B) per se violation
C) product design
D) industry concentration
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following has tended to reduce the importance of antitrust law, according to some economists?
A) industrial policy
B) conglomerate mergers
C) the rule of reason decision
D) rapidly changing technology
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What problem is created for antitrust regulators by online pricing algorithms?
A) Even if the algorithms produce collusive prices, the lack of an agreement makes it difficult to prosecute under current antitrust law.
B) The encrypted data does not allow regulators to determine whether prices are converging to a level consistent with collusion.
C) Online pricing algorithms are programmed to randomly vary prices to prevent antitrust regulators from discovering price-fixing.
D) Online pricing algorithms are programmed to ensure that there is just enough of a gap between prices across firms that collusion would be impossible to prove.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
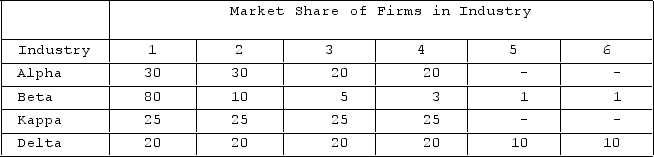 The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. A merger between Firm 2 and Firm 3 in Alpha would be a
The table shows market shares of firms in hypothetical industries. Assume these are distinct industries with no buyer-seller relationships or competition among them. A merger between Firm 2 and Firm 3 in Alpha would be a
A) vertical merger.
B) horizontal merger.
C) diagonal merger.
D) conglomerate merger.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which business practice is rarely challenged by the government under antitrust laws?
A) price-fixing
B) tying contracts
C) price discrimination
D) interlocking directorates
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Consider This box "Of Sea Fish and eBooks (and Other Things in Common) " lists examples of recent antitrust cases involving
A) monopolization.
B) tying contracts.
C) price-fixing.
D) horizontal mergers.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 264
Related Exams