A) the demand for money will increase.
B) the interest rate will fall.
C) bond prices will fall.
D) investment spending will increase.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If nominal GDP is $800 billion and, on average, each dollar is spent four times in the economy over a year, then the quantity of money demanded for transactions purposes will be
A) $200 billion.
B) $400 billion.
C) $800 billion.
D) $3,200 billion.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Federal Reserve will use an inflation rate target of 2 percent to
A) compensate for upward measurement bias in how the inflation rate is calculated.
B) allow for downward wage flexibility.
C) avoid the zero lower bound problem.
D) All of these choices are correct.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
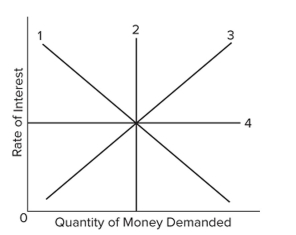 Which line in the graph would best illustrate the asset demand for money curve?
Which line in the graph would best illustrate the asset demand for money curve?
A) Line 1
B) Line 2
C) Line 3
D) Line 4
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A) decrease aggregate demand from AD
B) increase the money supply from $75 to $150 billion
C) increase interest rates from 4 to 8 percent
D) make no change in monetary policy
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why wouldn't the Fed want to drive nominal interest rates below zero in response to a financial crisis and recession?
A) Negative nominal interest rates would stimulate borrowing and spending, increasing aggregate demand.
B) Negative interest rates would stimulate so much lending that it would unfairly increase banks' power in the market.
C) Negative nominal interest rates would cause people to withdraw their money from banks, reducing what banks could lend out to consumers and businesses.
D) The Fed would lose the ability to raise the interest rates above zero in the future.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Since the 2008 financial crisis, borrowing at the federal funds rate
A) has dropped significantly because the rate has increased.
B) has replaced open-market operations as the most frequently used tool of monetary policy.
C) virtually never happens, as most banks have sufficient excess reserves.
D) has increased significantly, as banks struggle to maintain enough reserves.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The securities held as assets by the Federal Reserve Banks consist mainly of
A) corporate bonds.
B) Treasury bills, Treasury notes, and Treasury bonds.
C) common stock.
D) certificates of deposit.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If the Fed does a reverse repo of bonds with banks, then the banks' reserves will increase.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the given table, the equilibrium interest rate is
A) 2 percent.
B) 4 percent.
C) 6 percent.
D) 8 percent.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the cause-effect chain of an expansionary monetary policy?
A) A decrease in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase aggregate demand and GDP.
B) A decrease in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease aggregate demand and GDP.
C) An increase in the money supply will raise the interest rate, decrease investment spending, and decrease aggregate demand and GDP.
D) An increase in the money supply will lower the interest rate, increase investment spending, and increase aggregate demand and GDP.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the Taylor rule, if inflation is 3 percent and there is an unemployment gap of −2 percent, the Fed's targeted interest rate should be
A) 7.5 percent.
B) 3 percent.
C) 2 percent.
D) 1 percent.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the Federal Reserve authorities were attempting to reduce demand-pull inflation, the proper policies would be to
A) sell government securities, raise reserve requirements, raise the discount rate, and increase the interest paid on reserves held at the Fed banks.
B) buy government securities, raise reserve requirements, raise the discount rate, and reduce the amount of interest paid on reserves held at the Fed banks.
C) sell government securities, lower reserve requirements, lower the discount rate, and increase the interest paid on reserves held at the Fed banks.
D) sell government securities, raise reserve requirements, lower the discount rate, and increase the interest paid on reserves held at the Fed banks.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following best describes the effect of the zero interest rate policy implemented in December 2008?
A) Its effectiveness was limited by the zero lower bound problem.
B) It created a surge in inflation.
C) It forced nominal interest rates to below zero.
D) It had the desired effect, promoting full recovery by 2010.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bond with no expiration has an original price of $10,000 and a fixed annual interest payment of $1,000. If the price of this bond increases by $2,500, the interest rate in effect will
A) decrease by 1 percentage point.
B) decrease by 2 percentage points.
C) increase by 1 percentage point.
D) increase by 2 percentage points.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The Fed increases interest rates mainly by selling government securities.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The level of GDP, ceteris paribus, will tend to increase when
A) reserve requirements are increased.
B) there is an increase in the discount rate.
C) the Federal Reserve buys government securities in the open market.
D) the Federal Reserve sells government securities in the open market.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the amount of money demanded exceeds the amount supplied, the
A) demand-for-money curve will shift to the left.
B) money-supply curve will shift to the right.
C) interest rate will rise.
D) interest rate will fall.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In terms of the mechanics of quantitative easing,
A) quantitative easing formally changes interest rates; open-market operations only influence rates.
B) it works the same as open-market operations.
C) it differs from open-market operations in that the securities purchases occur directly from households.
D) it only changes the interest rate; it doesn't influence bank reserves.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lowering the reserve ratio
A) increases the total reserves in the banking system.
B) also reduces the discount rate.
C) turns required reserves into excess reserves.
D) reduces the amount of excess reserves the banks keep.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 361 - 380 of 405
Related Exams