A) 4 percent
B) −1.9 percent
C) 1.9 percent
D) 2.9 percent
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is associated with predictable inflation?
A) Tax distortions
B) Budget charges
C) Overheads
D) The re-distribution of purchasing power
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
According to the quantity theory of money, if there are fewer dollars available to spend on the same number of goods and services, then:
A) the price level will fall.
B) the price level will rise.
C) output will decrease.
D) output will increase.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the value of your debt decreases over time:
A) the real interest rate is negative.
B) inflation is zero.
C) the real interest rate is positive.
D) the real interest rate is zero.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the purchasing power of your debt increases over time:
A) the real interest rate is positive.
B) the nominal rate of interest is positive.
C) the inflation rate is greater than the nominal interest rate.
D) the real interest rate is negative.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is often the result of raising interest rates to control inflation?
A) Economic expansion
B) Economic contraction
C) Policy failure
D) An increase in firm investment
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The real interest rate is:
A) the federal funds rate.
B) adjusted for inflation.
C) the amount of interest the bank pays you for saving or charges you for borrowing.
D) the actual average interest rate in the economy.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The table shown provides CPI values for various years. 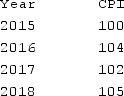 What was the inflation rate in 2018?
What was the inflation rate in 2018?
A) 2.9 percent
B) −1.9 percent
C) 1.9 percent
D) 4 percent
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the nominal interest rate?
A) The real interest rate adjusted for inflation
B) The reported interest rate adjusted for the effects of inflation
C) The lowest interest rate a bank will charge borrowers
D) The amount of interest the bank pays you for saving or charges you for borrowing
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the price of a key input increases suddenly, it causes:
A) cost-push inflation.
B) the business cycle to become sporadic.
C) demand-pull inflation.
D) the velocity of money to rise.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cost-push inflation occurs when the:
A) price of a key input increases suddenly.
B) price level changes in response to changes in the business cycle.
C) prices of necessity goods increase suddenly.
D) business cycle becomes sporadic and unpredictable.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Deflation is an overall:
A) rise in prices.
B) decline in prices.
C) rise in prices, excluding goods and services with historically volatile price changes.
D) decline in prices, excluding goods and services with historically volatile price changes.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To measure core inflation, the BLS excludes _______ from the basket of goods used to calculate the CPI.
A) food and energy
B) food, clothing, and housing
C) food and housing
D) housing and energy
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If an economy produces 2,000 units of output when the price level is $1 and the money supply is $1,000, what is the velocity of money?
A) 2
B) 500
C) 50
D) 5
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To measure core inflation, the BLS removes goods that:
A) have historically volatile prices.
B) have low elasticity.
C) have historically stable prices.
D) have high elasticity.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The idea that the value of money is determined by the overall quantity of money in existence is known as:
A) the quantity theory of money.
B) the dual mandate.
C) the price level requirement.
D) core inflation.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The number of transactions a typical dollar is used in during a given period is called the:
A) velocity of money.
B) transaction rate.
C) quantity theory of money.
D) monetary depreciation.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The reduction in aggregate demand caused by deflation:
A) further reduces prices, causing a deflationary spiral.
B) decreases production and raises prices back to their original level.
C) further reduces prices, causing aggregate supply to shift back to its long-run equilibrium.
D) decreases production and increase prices, mitigating the effects of the initial deflation.
F) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the purchasing power of your savings increases over time:
A) the real rate of interest is positive.
B) you'll be able to buy more with your savings in the future than you can now.
C) the inflation rate must be less than the nominal rate of interest.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The classical theory of inflation:
A) describes a long-run equilibrium.
B) explains the direct relationship between money supply and the price level.
C) shows the neutrality of money in the long run.
D) All of these statements are true.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 151
Related Exams