B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major disadvantage of the payback period method is it
A) Is useless as a risk indicator.
B) Ignores cash flows beyond the payback period.
C) Does not directly account for the time value of money.
D) All of the above are correct.
E) Only answers b and c are correct.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Using the discounted payback method, a project should be accepted when the discounted payback is greater than the projects expected life.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The capital budgeting director of Sparrow Corporation is evaluating a project which costs $200,000, is expected to last for 10 years and produce after-tax cash flows, including depreciation, of $44,503 per year.If the firm's required rate of return is 14 percent and its tax rate is 40 percent, what is the project's IRR?
A) 8%
B) 14%
C) 18%
D) −5%
E) 12%
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When Richard evaluated a capital budgeting project, a new machine needed to manufacture inventory using his firm's required rate of return, he discovered that the project's net present value (NPV) is negative.Based on this information, which of the following must be correct?
A) The project's internal rate of return is also negative.
B) The project's discounted payback period is greater than its economic life.
C) As long as the new machine's initial investment outlay is fairly low, the firm should purchase if it is used to replace an older machine that is required to produce inventory.
D) The project's traditional payback period must be greater than the maximum payback period that the firm has established.
E) Two or more of these scenarios must be correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
There exists an IRR solution for each time the direction of cash flows associated with project is interrupted.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a project's NPV exceeds the project's IRR, then the project should be accepted.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The NPV will be positive if the IRR is less than the required rate of return.
B) If the multiple IRR problem does not exist, any independent project acceptable by the NPV method will also be acceptable by the IRR method.
C) When IRR = r (the required rate of return) , NPV = 0.
D) The IRR can be positive even if the NPV is negative.
E) The NPV method is not affected by the multiple IRR problem.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A college intern working at Anderson Paints evaluated potential investments that is, capital budgeting projects using the firm's average required rate of return (WACC) , and he produced the following report for the capital budgeting manager: The capital budgeting manager usually considers the risks associated with capital budgeting projects before making her final decision.If a project has a risk that is different from average, she adjusts the average required rate of return by adding or subtracting 2 percentage points.If the four projected listed above are independent, which one(s) should the capital budgeting manager recommend be purchased?
A) Project LOM only, because it has both the highest NPV and the higher IRR.
B) Projects LOM, QUE, and YUP, because they all have positive NPVs and their IRRs.
C) Projects DOG and QUE, because their IRRs are greater than their risk-adjusted discount he projects returns are higher than the rates of return that capital budgeting manager uses to evaluate them.
D) Projects QUE, YUP, and DOG, because their IRRs are greater than their risk-adjusted discount rates that is, the projects returns are higher than the rates of return that capital budgeting manager uses to evaluate them.
E) There is not enough information to answer this question, because the firm's average required rate of return cannot be determined.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two projects being considered by a firm are mutually exclusive and have the following projected cash flows: Based only on the information given, which of the two projects would be preferred, and why?
A) Project A, because it has a shorter payback period.
B) Project B, because it has a higher IRR.
C) Indifferent, because the projects have equal IRRs.
D) Include both in the capital budget, since the sum of the cash inflows exceeds the initial investment in both cases.
E) Choose neither, since their NPVs are negative.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Seattle Corporation has been presented with an investment opportunity which will yield end of year cash flows of $30,000 per year in Years 1 through 4, $35,000 per year in Years 5 through 9, and $40,000 in Year 10.This investment will cost the firm $150,000 today, and the firm's required rate of return is 10 percent.What is the NPV for this investment?
A) $135,984
B) $18,023
C) $219,045
D) $51,138
E) $92,146
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Any capital budgeting investment rule should depend solely on forecasted cash flows and the opportunity rate of return.The rule itself should not be affected by managers' tastes, the choice of accounting method, or the profitability of other independent projects.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Conflicts between two mutually exclusive projects, where the NPV method chooses one project but the IRR method chooses the other, should generally be resolved in favor of the project with the higher NPV.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The involves comparing the actual results with those predicted by the project's sponsors and explaining why Any differences occur.
A) discounted payback
B) internal rate of return
C) post-audit
D) net present value
E) economic value added
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Woodson Inc.has two possible projects, Project A and Project B, with the following cash flows: . At what required rate of return do the two projects have the same net present value (NPV) ? (In other words, what is the "crossover rate" of the projects' NPV profiles?)
A) 10.3%
B) 13.5%
C) 15.8%
D) 21.7%
E) 34.8%
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Net present value is preferred to internal rate of return for capital budgeting decisions because
A) the internal rate of return does not allow you to determine if the project is acceptable.
B) the net present value is the only method that allows you to determine which independent project is acceptable.
C) the net present value allows you to compare mutually exclusive projects.
D) the internal rate of return for a project is different for each firm.
E) NPV contains information about a projects "safety margin" which is not inherent in IRR.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two fellow financial analysts are evaluating a project with the following net cash flows: One analyst says that the project has an IRR of between 12 and 13%.The other analyst calculates an IRR of just under 800%, but fears his calculator's battery is low and may have caused an error.You agree to settle the dispute by analyzing the project cash flows.Which statement best describes the IRR for this project?
A) There is a single IRR of approximately 12.7 percent.
B) This project has no IRR, because the NPV profile does not cross the X axis.
C) There are multiple IRRs of approximately 12.7 percent and 787 percent.
D) This project has two imaginary IRRs.
E) There are an infinite number of IRRs between 12.5 percent and 790 percent that can define the IRR for this project.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) There can never be a conflict between NPV and IRR decisions if the decision is related to a normal, independent project, i.e., NPV will never indicate acceptance if IRR indicates rejection.
B) To find the MIRR, we first compound CFs at the regular IRR to find the TV, and then we discount the TV at the required rate of return to find the PV.
C) The NPV and IRR methods both assume that cash flows are reinvested at the required rate of return. However, the MIRR method assumes reinvestment at the MIRR itself.
D) If you are choosing between two projects which have the same cost, and if their NPV profiles cross, then the project with the higher IRR probably has more of its cash flows coming in the later years.
E) A change in the required rate of return would normally change both a project's NPV and its IRR.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An increase in the discount rate used in computing the NPV of a project will lower the value of the NPV for that project.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Projects A and B have the same expected lives and initial cash outflows.However, one project's cash flows are larger in the early years, while the other project has larger cash flows in the later years.The two NPV profiles are given below: 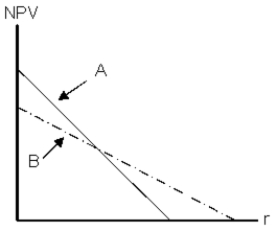 Which of the following statements is correct?
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Project A has the smaller cash flows in the later years.
B) Project A has the larger cash flows in the later years.
C) We require information on the required rate of return in order to determine which project has larger early cash flows.
D) The NPV profile graph is inconsistent with the statement made in the problem.
E) None of the above statements is correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 90
Related Exams