A) The number of cross-bridges that can form is higher in a short muscle fiber compared to longer fibers.
B) Muscle fibers that have larger diameters have more myofibrils and therefore can form more cross-bridges.
C) Increasing stimulation of a muscle fiber results in increased formation of cross-bridges.
D) Muscle fibers that are stretched to the optimal length will provide higher numbers of cross-bridges.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A toxin released by the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium botulinum causes the food-borne illness known as botulism, which inhibits the release of ACh at the neuromuscular junction. What effect does this have on a person infected with the bacterium?
A) It causes flaccid paralysis, and if it affects the respiratory muscles, can result in death.
B) It disrupts the balance between ACh and acetylcholinesterase, leading to spastic contractions.
C) The brain compensates by producing more ACh, limiting the illness to only a few hours.
D) The jaws are most affected, and it results in "lockjaw."
E) Problems only result when the individual has low immunity.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whales are air-breathing aquatic mammals, and some species can remain underwater for long periods of time. Which type of skeletal muscle fibers are most likely dominant in these deep diving whales?
A) Slow fibers
B) Fast (type IIa) fibers
C) Fast (IIb) fibers
D) White fibers
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
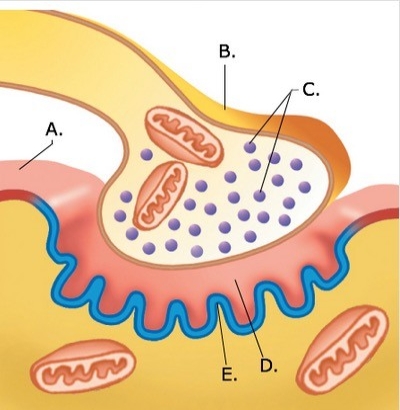 -The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "D" represent?
-The figure illustrates a detailed drawing of the neuromuscular junction. What does "D" represent?
A) Synaptic vesicles
B) Synaptic cleft
C) Sarcolemma
D) Presynaptic terminal
E) Postsynaptic membrane
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Anabolic steroids can do all of the following except
A) increase muscle size and strength.
B) cause testicular atrophy.
C) cause cardiovascular disease.
D) increase the number of muscle fibers.
E) increase total muscle mass.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following situations does a resting membrane potential exist?
A) A relaxed muscle fiber
B) A conducting neuron
C) A stimulated sensory receptor in the skin
D) A contracting cardiac muscle cell
E) The eye seeing an image
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue causes vasoconstriction?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
E) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following causes an unequal ion concentration across the resting plasma membrane?
A) The functioning of the sodium-chloride pump
B) Negatively charged proteins not readily diffusing across the plasma membrane
C) The attraction of chloride ions to other intracellular anions
D) The repulsion of potassium ions by the intracellular anions
E) The attraction of sodium ions to chloride ions
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Muscles exhibit the property of excitability. This means that the muscle
A) shortens its length.
B) recoils to its original resting length.
C) stretches beyond its normal length.
D) responds to stimulation by the nervous system.
E) excites itself.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During the contraction phase of a muscle twitch,
A) acetylcholine stimulates the pre-synaptic terminal.
B) Na+ diffuse into the muscle fiber.
C) actin-myosin cross-bridges form.
D) Ca2+ are transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
E) the action potential travels down the T tubule.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which fibers are primarily responsible for producing lactate?
A) Slow fibers
B) Type IIA fast fibers
C) Type IIB fast fibers
D) Type I slow-twitch fibers
E) Red fibers
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The electrical properties of cells are the result of
A) ion concentration differences across the plasma membrane.
B) receptor sites that are present on the plasma membrane.
C) phosphorylation reactions within the cytoplasm.
D) phospholipids in the plasma membrane.
E) None of these choices are correct.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The H zone
A) contains only myosin myofilaments.
B) contains only actin myofilaments.
C) contains both myosin and actin myofilaments.
E) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An antibody test on smooth muscle reveals fewer dense bodies and intermediate filaments in a patient with a colon disorder. What is the purpose of these structures?
A) They allow for rapidly developing action potentials in smooth muscle cells.
B) They are shallow invaginations of plasma membrane.
C) They maintain relatively constant tension in smooth muscle for a period of time.
D) They are part of the intracellular cytoskeleton.
E) They act as enzymes that remove phosphate from myosin.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Michael Jordan was arguably the best player in professional basketball history. Scientifically, one would expect him to have highly developed ________ fibers.
A) red
B) white
C) intermediate
D) fast twitch
E) slow oxidative
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Randy is participating in a strong man competition and is required to pull a yacht as far as he can. Which type of chemical process will his skeletal muscles rely on during this competition?
A) Anaerobic respiration
B) Aerobic respiration
C) Both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration are correct.
E) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not an important function of calcium ions in skeletal muscle activity?
A) Depolarization of the sarcolemma
B) Release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic terminal
C) Exposure of the active sites on G actin
D) All of these are important functions of calcium ions in skeletal muscle contraction.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Whole muscles can respond in a graded fashion to stimuli by varying
A) the force of contraction of individual muscle fibers.
B) the number of motor units recruited.
C) the amplitude of the action potential.
D) the frequency of stimulus.
E) thresholds.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inflammation of the fibrous connective tissue resulting in stiffness and soreness is
A) cramps.
B) fibrositis.
C) fibrosis.
D) muscular dystrophy.
E) paralysis.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a chemical that blocks the action of acetylcholinesterase. What effect does this have on muscles?
A) It would cause paralysis.
B) It would cause action potentials to be inhibited, thereby rendering the muscle useless.
C) The body would increase its production of acetylcholine to compensate.
D) The axons of the motor neurons would atrophy, and the muscle would weaken.
E) The muscle would have no way to relax, and spastic contractions would result.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 231
Related Exams