A) anisotropic band or A band
B) isotropic band or I band
C) muscle fiber
D) sarcomere
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A concentric contraction is described as
A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension during contraction.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension, but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An isometric contraction is described as
A) action potential frequency is high enough that no relaxation of muscle fibers occurs.
B) a muscle produces constant tension during contraction.
C) a muscle produces an increasing tension as the length remains constant.
D) a muscle produces increasing tension as it shortens.
E) a muscle produces tension, but the length of the muscle is increasing.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are similar in that they both
A) are under involuntary control.
B) are striated.
C) are widely distributed in the body.
D) have multiple nuclei.
E) are under voluntary control.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lack of acetylcholinesterase in the synaptic cleft would result in
A) a decrease in acetylcholine production by the motor neuron.
B) continuous stimulation of the postsynaptic membrane.
C) rapid degradation of acetylcholine.
D) relaxation of the muscle.
E) continuous stimulation of the presynaptic membrane.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
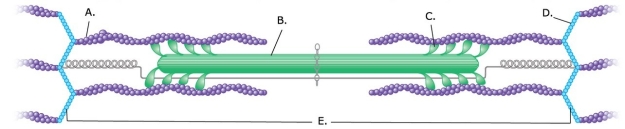 -What does "E" represent on the diagram?
-What does "E" represent on the diagram?
A) Myosin myofilament
B) Actin myofilament
C) Sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) Cross-bridge
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does "B" represent on the diagram?
-What does "B" represent on the diagram?
A) Myosin myofilament
B) Actin myofilament
C) Sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) Cross-bridge
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following structures contains the other four items listed?
A) Postsynaptic membrane
B) Presynaptic terminal
C) Synaptic cleft
D) Neuromuscular junction
E) Receptors on postsynaptic membrane
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -What does "D" represent on the diagram?
-What does "D" represent on the diagram?
A) Myosin myofilament
B) Actin myofilament
C) Sarcomere
D) Z disk
E) Cross-bridge
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rigor mortis occurs after death because
A) cross-bridges form but can't release.
B) Ca2+ is actively transported back to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) anaerobic respiration is occurring.
D) myosin levels decline at death.
E) cross-bridges never form.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following conditions in muscle fibers would contribute to muscle fatigue?
A) The emotional state of an individual
B) Depletion of ATP reserves
C) Inability of the motor neuron to produce sufficient quantities of acetylcholine
D) Depletion of neurotransmitter
E) Blocked receptors in the postsynaptic membrane
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
List the following structures in order from smallest to largest. (1) Muscle fiber (2) Myofilament (3) Myofibril (4) Muscle fascicle
A) 4, 2, 3, 1
B) 2, 1, 4, 3
C) 3, 1, 4, 2
D) 2, 3, 1, 4
E) 1, 2, 3, 4
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of muscle tissue causes contraction of the heart?
A) Skeletal muscle
B) Smooth muscle
C) Cardiac muscle
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
T tubules are invaginations of the
A) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) sarcomere.
C) myofibril.
D) sarcoplasm.
E) sarcolemma.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Physiological contracture
A) occurs when muscles are resting.
B) is a condition in which cross-bridges cannot release.
C) is caused by an abundance of ATP in muscle fibers.
D) results when muscles are well exercised.
E) results when the neurotransmitter remains in the receptor.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The training regimen of a competitive weight lifter is designed partly to
A) convert certain muscles with parallel muscle fascicles into muscles with non-parallel muscle fascicles.
B) increase the average number of myofibrils per muscle fiber.
C) convert fast muscle fibers to slow muscle fibers.
D) increase the size of his motor units.
E) lower the threshold for muscle stimulation.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The time between application of the stimulus to a motor neuron and the beginning of contraction is called the ________ phase.
A) contraction
B) relaxation
C) latent or lag
D) refractory
E) threshold
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In order for muscle relaxation to occur,
A) Ca2+ must be transported to troponin.
B) power strokes slow down.
C) the active sites on actin must be blocked.
D) Na+ must be actively transported to troponin.
E) the active sites on myosin must be uncovered.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A sarcomere is the
A) plasma membrane of a muscle fiber.
B) cytoplasm of a muscle fiber.
C) structural and functional unit of the skeletal muscle fiber.
D) contractile thread that extends the length of the muscle fiber.
E) protein strand composed of actin or myosin.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As you are lifting a box, someone places extra weight on top of it. For your muscle to continue contracting and lifting the box, the muscle must
A) recruit more muscle fibers.
B) lower its threshold.
C) reduce its wave summation.
D) shift from isometric to isotonic contraction.
E) shift from slow-twitch to fast-twitch mode.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 201 - 220 of 231
Related Exams