A) Damage to the spinothalamic pathway
B) Lack of decussation in the fasciculus gracilis tract of the dorsal column medial lemniscal pathway
C) Damage to the anterior spinocerebellar pathway
D) Damage to the tectospinal pathway
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these combinations of general senses depends on mechanoreceptors?
A) Touch and temperature
B) Pressure and temperature
C) Pressure and proprioception
D) Proprioception and temperature
E) Taste and smell
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The senses of taste and hearing both utilize receptor cells that are categorized as ________.
A) primary receptors
B) secondary receptors
C) mechanoreceptors
D) chemoreceptors
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -Corpus callosum
A) The part of the brain involved in actual declarative memory
B) The largest of the cerebral commissures
C) A factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) A series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) A part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The portion of the dorsal column/medial lemniscal tract that carries proprioceptive sensations from nerve endings in the feet and legs is the ________.
A) nucleus gracilis
B) nucleus cuneatus
C) fasciculus gracilis
D) fasciculus cuneatus
E) fasciculus nucleus
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the sensation with the appropriate receptor type. -Ruffini end organs
A) Mechanoreceptors
B) Thermoreceptors
C) Nociceptors
D) Chemoreceptors
E) Photoreceptors
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The simplest and most common type of sensory nerve endings are free nerve endings.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
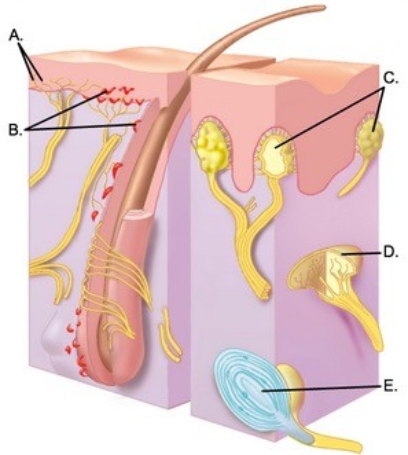 -The diagram illustrates sensory receptors in the skin. What structure does "D" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) Free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
-The diagram illustrates sensory receptors in the skin. What structure does "D" represent?
A) Meissner corpuscles
B) Free nerve endings
C) Ruffini end organ
D) Pacinian corpuscle
E) Merkel disks
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would you observe in a patient with a tumor of the cerebellum?
A) Loss of general sensation
B) Balance impairment
C) No heartbeat
D) Increased sex drive
E) No conscious thought
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The primary somatosensory cortex is located in the ________ lobe.
A) frontal
B) temporal
C) occipital
D) parietal
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Brain waves associated with information processing or problem solving are ________ waves.
A) alpha
B) beta
C) delta
D) theta
E) kappa
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The sense of taste is an example of a general sense.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rapidly adapting proprioceptors that provide information on the location of a moving hand are known as ________ receptors.
A) phasic
B) primary
C) secondary
D) tonic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a descending pathway in the spinal cord?
A) Fasciculus gracilis
B) Corticospinal tract
C) Spinothalamic tract
D) Spinoreticular tract
E) Trigeminothalamic tract
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
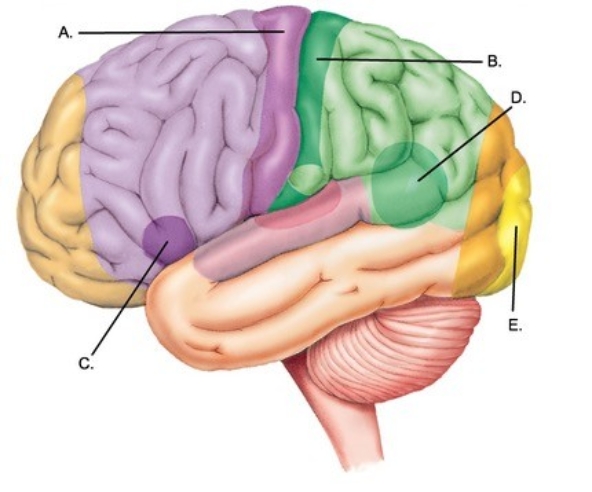 -Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
A) Visual cortex
B) Primary motor cortex
C) Primary somatosensory cortex
D) Motor speech area (Broca area)
E) Sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
-Label area "A" on the cerebral cortex.
A) Visual cortex
B) Primary motor cortex
C) Primary somatosensory cortex
D) Motor speech area (Broca area)
E) Sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
 -Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
A) Visual cortex
B) Primary motor cortex
C) Primary somatosensory cortex
D) Motor speech area (Broca area)
E) Sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
-Label area "B" on the cerebral cortex.
A) Visual cortex
B) Primary motor cortex
C) Primary somatosensory cortex
D) Motor speech area (Broca area)
E) Sensory speech area (Wernicke area)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following tract is mismatched with its description?
A) Spinotectal tract - visual reflexes
B) Fasciculus cuneatus - vibration from upper body half
C) Spinoreticular tract - light touch
D) Spinocerebellar tract - proprioception
E) Spinocerebellar tract - comparator function
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The extrapyramidal system
A) controls the speed of skilled movements.
B) maintains control of unconscious movements.
C) interprets cutaneous perception.
D) projects sensory information from the medulla to the cerebrum.
E) control facial expression, mastication, and tongue movements.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The conscious perception of cutaneous sensations occurs in the cerebral cortex, but these sensations are perceived as if they were on the surface of the body. This is called ________.
A) association
B) perception
C) projection
D) integration
E) localization
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The right cerebral hemisphere
A) receives sensory input from the left side of the body.
B) is the dominant hemisphere for speech in most people.
C) tends to be smaller than the left cerebral hemisphere.
D) contains no association areas.
E) is not connected to the left cerebral hemisphere.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 149
Related Exams