A) Corticospinal tract - movements, especially the hands
B) Corticobulbar tract - movements in the head and face
C) Rubrospinal tract - two-point discrimination
D) Vestibulospinal tract - maintains upright posture
E) Reticulospinal - posture adjustments and walking
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A primary function of the cerebellum is to ________.
A) interpret sound
B) coordinate movement
C) control body temperature
D) regulate consciousness
E) regulate sleep patterns
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Damage to the cerebellum is likely to cause
A) decreased muscle tone.
B) balance impairment.
C) the tendency to overshoot when reaching for an object.
D) an intention tremor.
E) All of the choices are correct.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match the term with its definition. -Memory engram
A) The part of the brain involved in actual declarative memory
B) The largest of the cerebral commissures
C) A factor than activates gene transcription for formation of dendritic spines
D) A series of neurons involved in long-term memory
E) A part of the temporal lobe involved in adding emotional overtones to a memory
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The gate control theory of pain says that pain impulses traveling through the lateral spinothalamic tract can be suppressed by increased activity of the
A) anterior spinothalamic tract.
B) tertiary neurons.
C) extrapyramidal tracts.
D) dorsal column/medial lemniscal system.
E) spinocerebellar tracts.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Abby is trying to focus on her A&P exam, but she feels something crawling along the back of her arm. Alarmed, she jumps up and brushes away a small spider. Which of the following does Abby have to thank for alerting her to this issue?
A) Spinothalamic tract
B) Fasciculus gracilis tract
C) Spinocerebellar pathway
D) Tectospinal tract
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
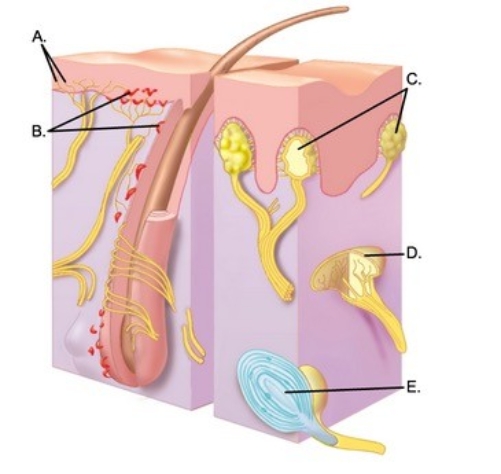 -What is the function of the sensory receptor of the skin labeled "C"?
A) Detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) Responds to painful stimuli
C) Responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) Detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) Detects continuous touch or pressure
-What is the function of the sensory receptor of the skin labeled "C"?
A) Detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) Responds to painful stimuli
C) Responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) Detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) Detects continuous touch or pressure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
CREB activates gene transcription in neurons that results in the formation of ________.
A) myelin sheath
B) dendritic spines
C) more receptors
D) All of the choices are correct.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
 -What is the function of the sensory receptor of the skin labeled "E"?
A) Detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) Responds to painful stimuli
C) Responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) Detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) Detects continuous touch or pressure
-What is the function of the sensory receptor of the skin labeled "E"?
A) Detects deep pressure, vibration, and proprioception
B) Responds to painful stimuli
C) Responds to light touch and superficial pressure
D) Detects touch, involved in 2-point discrimination
E) Detects continuous touch or pressure
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The region of the limbic system that is involved in the feeling of satisfaction with sex and feeding behaviors is the ________.
A) amygdala
B) cingulate gyrus
C) hippocampus
D) thalamus
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A person suffering a stroke in the right parietal lobe may lose the ability to recognize faces. This is called ________.
A) aphasia
B) apraxia
C) athetosis
D) amorphosynthesis
E) incoherency
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Select the statements that describe lower motor neurons. (Check all that apply.)
A) Have axons extending into peripheral nerves
B) Send signals to skeletal muscles
C) Send signals to visceral smooth muscle
E) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A baseball pitcher was hit on the side of the head by a line drive. When he was revived, he could not remember how many balls and strikes the batter had. This was because
A) short-term memory had not been converted to working memory.
B) he lost both working and short-term memory.
C) long-term memory had not been converted to working memory.
D) he lost long-term memory.
E) None of the choices are correct.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A lesion in the red nucleus results in ________ tremors.
A) resting
B) intention
C) sleeping
D) reflex
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In short-term memory,
A) information is retained for less than a second.
B) the frontal lobe plays the most important role.
C) current information is lost when new information is presented.
D) there is increased synaptic activity by long-term potentiation.
E) there is consolidation of information.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Trina, a 72-year-old retired nurse, presents with the following: difficulty swallowing, easily fatigued, impaired gag reflex. Which of the symptoms is most likely the result of aging?
A) Easily fatigued
B) Difficulty swallowing
C) Impaired gag reflex
D) None of the choices are correct.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Wernicke area is necessary for
A) motivation.
B) understanding and formulating coherent speech.
C) initiating the muscular movements of speech.
D) processing visual images.
E) smiling.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A patient with a lesion in the hippocampus may have decreased ________.
A) sensory memory
B) Pavlovian reflexes
C) procedural memory
D) declarative memory
E) short term memory
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a general sense?
A) Smell
B) Taste
C) Touch
D) Hearing
E) Vision
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Lesions of the limbic system might result in
A) a voracious appetite.
B) enhanced fear and anger responses.
C) decreased sexual activity.
D) loss of coordination.
E) loss of sensation.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 149
Related Exams