A) the sum of the expenses of the firm that vary directly with the quantity of a product that is produced and sold.
B) the total expense incurred by a firm in producing and marketing a product, which equals the sum of overhead cost and variable cost.
C) the sum of the expenses of the firm that are stable and do not change with the quantity of a product that is produced and sold.
D) the average amount of money received for selling one unit of a product or simply the price of that unit.
E) the change in expenses that results from producing and marketing one additional unit of a product.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements about price elasticity of demand is most accurate?
A) The more substitutes a product has, the more likely it is to be price elastic.
B) All products show some price inelasticity.
C) Nondiscretionary (necessary) purchases are price elastic.
D) With inelastic demand, reducing price has a very large impact on revenues.
E) With inelastic demand, manufacturers change prices frequently to capitalize on consumer behavior.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pure competition is the competitive situation in which
A) many sellers follow market price for identical, commodity products.
B) one seller sets the price for a unique product.
C) few sellers are sensitive to one another's prices.
D) many sellers compete on nonprice factors.
E) one or few sellers compete solely on nonprice factors.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
VIZIO's HDTVs are sold through all of these types of retailers exceptwhich?
A) Amazon.com
B) mass merchandisers, such as Target
C) its own brick-and-mortar stores
D) wholesale club stores such as Sam's Club
E) electronics stores such as Best Buy
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When estimating demand, price is not the only factor to be considered. Three other elements are emphasized by economists, one of which is
A) consumer tastes.
B) legislative changes.
C) size of the target market.
D) current political stability.
E) promotional methods.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Washburn Guitars markets its guitars to four distinct market segments. The firm's batch-custom instruments are targeted at
A) first-time buyers.
B) professional musicians.
C) celebrities.
D) large institutional buyers such as band programs.
E) intermediate-skill players who may become professional musicians.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
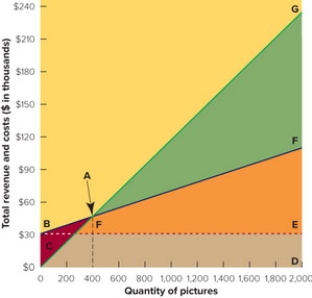 Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the triangular area GAF represents the firm's
Figure 13-7B
-In the break-even chart in Figure 13-7 above, the triangular area GAF represents the firm's
A) fixed costs.
B) break-even point.
C) variable costs.
D) profit.
E) total revenue.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
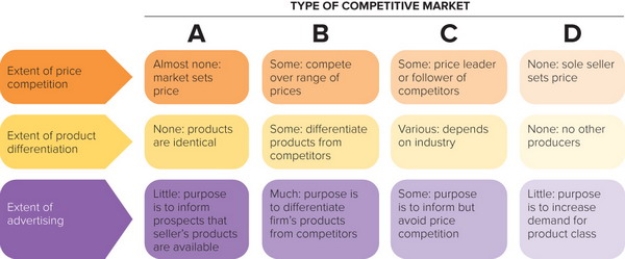 Figure 13-3
-In Figure 13-3 above, column B represents which type of competitive market?
Figure 13-3
-In Figure 13-3 above, column B represents which type of competitive market?
A) an oligopoly
B) monopolistic competition
C) a pure monopoly
D) pure competition
E) oligopolistic competition
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Marketers may engage in value pricing, which is the practice of simultaneously ________ while maintaining or decreasing price.
A) promoting specific product and service benefits
B) increasing product and service benefits
C) decreasing profit
D) analyzing benefits
E) decreasing cost
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If competitive market circumstances are such that there is no price competition, no product differentiation, and the purpose of advertising is to increase demand for the product class, then ________ must exist in the industry.
A) an oligopoly
B) monopolistic competition
C) a pure monopoly
D) pure competition
E) oligopolistic competition
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Three different pricing objectives relate to a firm's profit. One objective, known as ________, is common in many firms because the targets can be set and performance measured quickly though sometimes criticized for its short-term orientation.
A) managing for long-run profits
B) target return
C) break-even strategy
D) maximizing current profit
E) minimizing risk
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The competitive market situation in which many sellers compete on nonprice factors is referred to as
A) a pure monopoly.
B) an oligopoly.
C) pure competition.
D) monopolistic competition.
E) monopolistic oligopoly.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these best illustrates a shift in the demand curve?
A) When prices remain the same, there is a significant change in supply.
B) As the price is raised, the quantity demanded increases, assuming all else stays the same.
C) When prices remain the same, there is an increase or decrease in demand.
D) As the price is lowered, the quantity demanded decreases, assuming all else stays the same.
E) An internal matter has forced a price change of some type, but it does not impact demand.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When it was launched, the BMW Streetcarver was the only skateboard with stabilizers and wheel design based on BMW's automobiles. This technology gave the BMW Streetcarver better control at high speeds and around sharp turns than any other brand. The skateboard was priced at $495, which left many consumers (especially young males) who might have wanted to buy the Streetcarver unable to afford it. This inability to pay for the high-priced BMW-made skateboard shows the effect of ________ on sales.
A) demand factors
B) macroeconomic environmental factors
C) barter factors
D) supply factors
E) exchange parameters
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
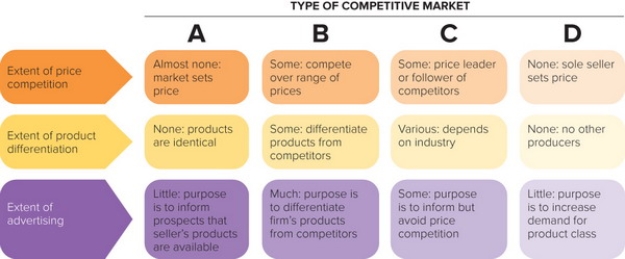 Figure 13-3
-In Figure 13-3 above, column D represents which type of competitive market?
Figure 13-3
-In Figure 13-3 above, column D represents which type of competitive market?
A) an oligopoly
B) monopolistic competition
C) a pure monopoly
D) pure competition
E) oligopolistic competition
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements about consumer demand as a pricing constraint is most accurate?
A) The price charged by competitors for similar offerings has little effect on the price a seller can charge unless there are very few potential buyers.
B) The number of potential buyers for the product affects the price a seller can charge, but only if the product is using a push strategy in the channel.
C) The number of potential buyers for the product affects the price a seller can charge, but only if the product is a necessity item.
D) The number of potential buyers for the brand affects the price a seller can charge in the growth stage of a product life cycle, but not in the introductory stage.
E) The number of potential buyers generally affects the price a seller can charge.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many cosmetology schools allow their advanced students to style hair for "real-world" clients for a reduced fee. The students benefit from the experience, the clients get a less expensive haircut, and the school provides students with additional training while generating revenue as well. The haircut pricing is an example of
A) value pricing.
B) societal pricing.
C) revenue sharing.
D) barter.
E) cost-assist pricing.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A maximizing current profit pricing objective implies that a company chooses to
A) set targets for which performance can be measured quickly.
B) give up immediate profit in exchange for achieving a higher market share in hopes of penetrating competitive markets.
C) set a profit goal that is often determined by its board of directors.
D) reduce investment in any further market or product research.
E) set prices based on return on sales.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A break-even chart is a graphic presentation
A) that shows the maximum number of units that will be sold at a certain price.
B) of a break-even analysis that shows when total revenue and total cost intersect to identify profit or loss for a given quantity sold.
C) that relates variable costs in terms of product or service substitutes in order to determine which items or services would least affect total revenues.
D) that relates profits and revenues versus total costs in order to determine the time frame in which a company could achieve profitability.
E) of a form of scatter graph used to identify specific activities or items that are creating the greatest return on investment.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements regarding price changes is most accurate?
A) Prices for tangible goods should change monthly, whereas service prices should change quarterly.
B) Changing a product's price too frequently creates antagonism among consumers, yet changing prices too infrequently makes them feel the company is not improving its product sufficiently.
C) Supermarkets should change their prices every week since customers are expecting new prices in the weekly flyers they receive in the mail.
D) Companies selling products online can instantly change their prices whenever the need arises.
E) Internet price changes are regulated by the Internet Fair Practices Act to protect consumers against price gouging.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 237
Related Exams