A) Müllerian
B) competitive
C) Batesian
D) aposematic
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Alligators excavate holes in the bottom of bodies of water.During times of severe drought these holes act as refugia for various aquatic organisms that might perish if there were no water available.Thus,alligators in this system can be classified as a(n)
A) keystone species.
B) symbiotic species.
C) sympatric species.
D) allopatric species.
E) refugistic species.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Based on the following graph,what is the most likely relationship between Paramecium and Didinium? 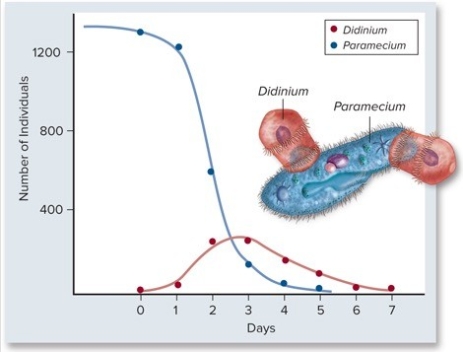
A) Paramecium prey on Didinium.
B) Paramecium have a commensal relationship with Didinium.
C) Didinium and Paramecium have a mutualistic relationship.
D) Didinium prey on Paramecium.
E) Paramecium is a parasite that feeds on Didinium.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following examples would be undergoing secondary succession? Check all that apply.
A) an abandoned potato farm
B) a coastal grassland damaged by a hurricane
C) an abandoned landfill
D) rocks in a national park covered by mosses and lichens
E) a garden bed that has been weeded
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Geographical allopatry between species is definitive evidence of interspecific competition.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Chemicals that play the dominant role in protecting plants from being eaten by herbivores or predators are called
A) primary compounds.
B) secondary compounds.
C) poisons.
D) oils.
E) amino acids.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two of Darwin's finches display a character displacement when they occur as sympatric species.Which of the statements correctly interprets the graph? 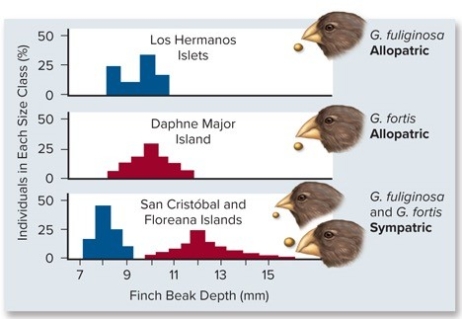
A) Both species have the same size beak on Santa Maria Island.
B) Both species have the same size beaks on Daphne Major.
C) Both species have the same size beaks on Los Hermanos Island.
D) The two species have different beak sizes when they occur on the same island.
E) The two species feed on different food resources; one feeds on seeds while the other feeds on insects.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Following their respective breeding seasons,several species of hummingbirds occur at the same locations in North America and several hummingbird flowers bloom simultaneously in these habitats.These flowers seem to have converged to a common morphology and color.Birds have the most visual sensitivity to the color red.Following their breeding season,these species of hummingbirds are
A) allopatric.
B) sympatric.
D) undefined
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
It is a situation in which a palatable organism resembles another kind of organism that is distasteful or toxic.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The difference in the fundamental niche and the realized niche is
A) the fundamental niche is the actual niche that a species occupies while the realized niche is the potential area that the species is capable of inhabiting.
B) the fundamental niche is the entire niche that a species is capable of using while the realized niche is just what is being occupied.
C) the fundamental niche is smaller than the realized niche.
D) the realized niche is theoretical while the fundamental niche is the entire niche that an organism can use.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In ________ mimicry,two or more unrelated but protected species resemble one another,thus achieving a kind of group defense.
A) Batesian
B) disruptive
C) Müllerian
D) cooperative
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A relationship in which both members benefit is called
A) predation.
B) parasitism.
C) mutualism.
D) commensalism.
E) sympatric.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of commensalism?
A) a tapeworm living in the intestines of a mule deer
B) barnacles hitching a ride on the skin of a whale
C) a female mosquito sucking blood from a musk oxen
D) wood-digesting flagellates living in the gut of termites
E) acacia trees and their ants
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about mimicry are true? Check all that apply.
A) Generally,the number of mimics in a Müllerian mimicry system must be less than the number of models
B) Only Batesian mimicry depends on the ability of the predator to learn.
C) In Müllerian mimicry,the participants are both mimics and models.
D) In Batesian mimicry,the participants are either mimics or models.
E) A Müllerian mimic is "a sheep in wolf's clothing."
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In studies of two species of barnacles in the marine intertidal zone it was observed that Chthamalus can live in the upper intertidal zone and the lower intertidal zone if Semibalanus is absent,and Semibalanus can only live in the lower zone because it is more subject to dehydration.Based on this,which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply.
A) The realized niches of the two species differ.
B) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than its realized niche.
C) The fundamental niche of Chthamalus is larger than the fundamental niche of Semibalanus.
D) The fundamental and the realized niches of Chthamalus are the same.
E) The fundamental and the realized niches of Semibalanus are the same.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In general,communities in early succession will be dominated by fast-growing species with r-selected life histories.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Communities evolve to have greater biomass and species richness in a process called
A) sympatric interactions.
B) adaptive modifications.
C) succession.
D) symbiotic relationships.
E) competitive exclusion.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Paleontological studies indicate that,over millions of years,
A) groups of species that have coevolved rise and go extinct together.
B) species that occurred together in the distant past still occur together today; the community has held constant.
C) the extinction of species is not related to the community in which they lived.
D) species seem to come and go individually as niches within a community become available.
E) species richness is constant over time.
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Interspecific competition can affect the phenotypic characteristics of organisms.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Succession happens because species in the habitat alter that habitat in ways that assist other species.There are three dynamic concepts that are of critical importance for succession to take place.They are
A) establishment,facilitation,and inhibition.
B) symbiotic relationships,facilitation,and aposematic coloration.
C) establishment,coevolution,and competitive exclusion.
D) competition,climax communities,and tolerance.
E) competition,inhibition,and coevolution.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 59
Related Exams